Home > Press > Using sound to independently levitate a range of objects is achieved for the first time
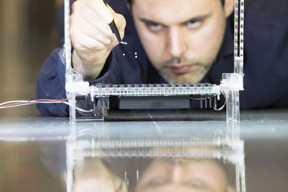 |
| The researcher Asier Marzo, who carried out this project, checks the strength of the acoustic traps. CREDIT Sergio Larripa, Asier Marzo and Bruce Drinkwater. |
Abstract:
This research, which has been funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) in the United Kingdom, has just been published in the scientific journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, the official publication of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States.
Using sound to independently levitate a range of objects is achieved for the first time
San Sebastian, Spaiin | Posted on December 28th, 2018Sound can exert force on objects. When ultrasonic waves are used and when the volume is increased considerably, scientists can create an acoustic field capable of moving a whole range of small-sized objects. The new algorithm developed by the team of researchers enables sufficiently complex acoustic fields to capture numerous objects in the desired positions.
Advantages of acoustic tweezers
These acoustic tweezers have capabilities similar to those of the optical tweezers that won the Nobel Prize in Physics this year and which use lasers to capture and transport microparticles. Yet acoustic tweezers offer various advantages over optical tweezers.
Lasers can only travel through transparent mediums, which makes it complicated for them to be used in applications inside biological tissue. By contrast, ultrasound is routinely used in pregnancy ultrasound scanning and in treating kidney stones, as it can penetrate tissue safely and non-invasively.
Another advantage is that acoustic devices are 100,000 times more efficient than optical systems. "Optical tweezers are a fantastic technology, but they always come dangerously close to killing the cells they manipulate. By contrast, the acoustic version enables us to generate forces with the same magnitude but with much less energy. There are many applications that call for cell manipulation, and acoustic systems are perfect for that," pointed out Prof Drinkwater, lecturer in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at the University of Bristol.
To demonstrate the precision of their system, the scientists stuck two millimetre-sized spheres to the ends of a thread and used the acoustic tweezers to "sew" the thread into a piece of fabric. The system can simultaneously control the 3D movement of up to 25 particles in the air. The team hopes that the technique could be adapted to the manipulation of particles in water within approximately one year. Shortly afterwards, it could be adapted for use in biological tissue.
"The flexibility of the ultrasound waves enables us to operate on micrometric scales to move cells within printed 3D structures or living tissue," explained Asier Marzo. "But we can also work on a larger scale, for example, to levitate tangible pixels that form various objects in the air." These objects comprising levitating particles that can be observed by several people from different angles are also susceptible to being touched and manipulated directly; in other words, one can use one's hands to drag them. "We are used to two-dimensional pixels enclosed in our monitors, but we would like to see a technology in which objects are made up of tangible pixels that float in mid-air," added the researcher in the Department of Statistics, Computing and Mathematics of the Public University of Navarre.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Oihane Lakar Iraizoz
0034-943-363-040
Copyright © Elhuyar Fundazioa
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








