Home > Press > Scientists verify a way of how to improve resolution of most powerful microscopes: The resolution and intensity of powerful nanoscopes could be enhanced by over 30% via non-spherical particle lenses
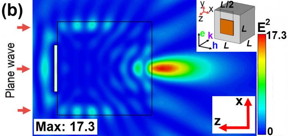 |
| Simulated near-field E 2 field enhancement distribution on xz plane with the amplitude mask apodization. CREDIT Tomsk Polytechnic University |
Abstract:
Researchers from Tomsk Polytechnic University (Russia) and Bangor University (UK) have experimentally verified anomalous amplitude apodization for non-spherical particles for the first time. This phenomenon makes it possible to boost the magnifying power of microscopes and to more effectively record molecules and viruses. The study results were reported in Journal of Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves.
Scientists verify a way of how to improve resolution of most powerful microscopes: The resolution and intensity of powerful nanoscopes could be enhanced by over 30% via non-spherical particle lenses
Tomsk, Russia | Posted on May 1st, 2018"If we mask part of an ordinary lens surface with an optical filter, it will increase the magnifying power of the lens. But peak field intensity drops dramatically. The same effect is typical of spherical particle-lenses in nano-scopes or high-definition optical microscopes with a magnifying power of 50 nanometers. If we use non-spherical particles, including cylinders with illuminated butt-ends, as lenses, and if we mask part of the surface, it will simultaneously boost their magnifying power and peak field intensity. This is called the amplitude mask apodization effect," Professor Igor Minin from Tomsk Polytechnic University's faculty of electronic engineering noted.
Non-spherical particles function as super-lenses accumulating evanescent (damp) waves that can form an image with unprecedentedly high definition levels.
In their work, scientists cite experimental data confirming the existence of the amplitude mask apodization effect in the millimeter waveband. During their experiments, cuboid dielectric particles, part of whose surfaces (about 45 percent) are covered with a copper amplitude mask, showed a 36-percent increase in magnifying power, with peak field intensity levels increasing by over 30 percent.
You could say that spherical particle-lenses boost the magnifying power of nano-scopes only through the loss of energy. But when we use non-spherical particles, the magnifying power increases at a rate commensurate with the greater peak field intensity levels," Minin added. The long-term development of this technique will make it possible to obtain images of large biological molecules, viruses and the internal elements of living cells using non-spherical particles.
Experts will no longer have to painstakingly prepare various samples. For example, this is an important aspect of fluorescent microscopy. The amplitude mask apodization effect has a wide range of applications where sub-wavelength focusing is required. These are medicine, non-destructive testing, flaw detection, on chip processing and data transfer systems, etc.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kristina Nabokova
7-382-270-5685
Copyright © Tomsk Polytechnic University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








