Home > Press > How to build a better railway -- in (almost) every cell in your body
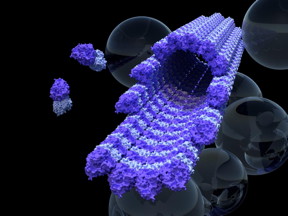 |
| This is a single microtubule 'railway track' surrounded by bubbles of 'cargo' held inside cells. CREDIT University of Warwick |
Abstract:
New work from the University of Warwick shows how a microscopic 'railway' system in our cells can optimise its structure to better suit bodies' needs.
How to build a better railway -- in (almost) every cell in your body
Coventry, UK | Posted on March 13th, 2018The work was conducted by Professor Robert Cross, director of the centre for mechanochemical cell biology at Warwick Medical School and leader of the Cross lab.
His team based at Warwick Medical School has been looking at how the microtubule 'railway tracks' inside cells are built. Almost every cell in our bodies contains a 'railway' network, a system of tiny tracks called microtubules that link important destinations inside the cell. Professor Cross' team found the system of microtubule rails inside cells can adjust its own stability depending on whether it is being used or not..
Prof Cross said: "The microtubule tracks of the cellular railway are almost unimaginably small - just 25 nanometres across (a nanometre being a millionth of a millimetre).The railway is just as crucial to a well-run cell as a full-size railway is to a well-run country. For cells and for countries the problem is very much the same - how to run a better railway?"
"Imagine if the tracks of a real railway were able to ask themselves, 'am I useful?' To find out, they would check how often a railway engine passed along them.
"It turns out that the microtubule railway tracks inside cells can do exactly that - they check whether or not they are in contact with tiny railway engines (called kinesins). If they are, then they remain stably in place. If they are not, they disassemble themselves. We think this allows the sections of microtubule rail to be recycled to build new and more useful rails elsewhere in the cell."
The paper, 'Kinesin expands and stabilizes the GDP-microtubule lattice' published (12 March 2018) in Nature Nanotechnology, shows that when the kinesin railway engines contact their microtubule rails, they subtly change their structure, producing a very slight lengthening that stabilises the rail.
Using a custom built microscope, the Warwick Open Source Microscope, the researchers who are also based at Warwick Systems Biology Centre and Mathematics Institute, University of Warwick, detected a 1.6% increase in the length of microtubules attached to kinesins, with a 200 times increase in their lifetime.
By revealing how microtubules are stabilised and destabilised, the team hope to throw new light on the workings of a number of human diseases (for example Alzheimer's), which is linked to abnormalities in microtubule function. They are hopeful also that their work may ultimately lead to improved cancer therapy because the railway is so vital (for example for cell division), as its microtubule tracks are a key target for cancer drugs such as Taxol. Exactly how Taxol stabilises microtubules in cells remains poorly understood.
Professor Cross added: "Our new work shows that the kinesin railway engines stabilise microtubules in a Taxol-like way. We need to understand as much as we can about how microtubules can be stabilised and destabilised, to pave and illuminate the road to improved therapies."
###
The research was funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council via the Systems Biology Doctoral Training Centre, University of Warwick; and the Wellcome Trust.
Kinesin expands and stabilizes the GDP-microtubule lattice published in Nature Nanotechnology
Authors
Daniel R. Peet: Centre for Mechanochemical Cell Biology, Warwick Medical School, Coventry, UK; Warwick Systems Biology Centre, University of Warwick, Coventry, UK
Nigel J. Burroughs: Warwick Systems Biology Centre, University of Warwick, Coventry, UK; Mathematics Institute, University of Warwick, Coventry, UK
Robert A. Cross Centre for Mechanochemical Cell Biology, Warwick Medical School, Coventry, UK
Funding
This research was funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (grant number BB-G530233-1) via the Systems Biology Doctoral Training Centre, University of Warwick; and the Wellcome Trust (grant number 103895/Z/14/Z).
The DOI for this paper is 10.1038/s41565-018-0084-4
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Nicola Jones
07-920-531-221
Copyright © University of Warwick
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








