Home > Press > Tiny bubbles provide tremendous propulsion in new microparticles research-Ben-Gurion U.
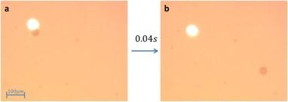 |
| Caption: Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers demonstrate a light-generated bubble for microparticle propulsion. Panel (a) shows the 42?μm diameter spherical particle and the 405?nm laser beam as the respective dark and bright patches. Panel (b) shows that 40 milliseconds later the microsphere has traversed a distance roughly 10 times its size. CREDIT Ben-Gurion U. |
Abstract:
An innovative technique using light and tiny bubbles to propel microparticles at forces many times greater than previously achieved has been developed by Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers.
Tiny bubbles provide tremendous propulsion in new microparticles research-Ben-Gurion U.
Beer-Sheva, Israel | Posted on June 21st, 2017The new technique could have significant implications in the development of micromotors and optical devices for use in solar cell optics. "What we ultimately hope to achieve is a highly accurate, passive technology for use in a concentrated solar device that would follow the sun without the need for a mechanical tracking mechanism," says Dr. Avi Niv, study co-author.
According to the findings published recently in Nature Scientific Reports, the researchers converted the energy created from light into kinetic motion using nano-sized, laser-generated bubbles. As the bubble expands it acts as a propulsion mechanism for surrounding microparticles. Mechanical manipulation of micro- and nano-scaled objects is important in biology, surface science and microfluidics, and for micromachines in general.
View a video of the experiment. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fL9CUoSkYeU
Dr. Niv says, "In our study, a micron-sized object was propelled at unprecedented speeds of close to one meter-per-second, six times faster than what is common in present devices, while still maintaining motion direction control." Dr. Niv and co-author Ido Frenkel, a Ph.D. student, are part of BGU's Alexandre Yersin Department of Solar Energy and Environmental Physics at the Jacob Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research.
"After the bubble initiates movement and bursts, there is no trace of the vapor; the system returns to the original state and the same action can be initiated repeatedly, like a combustion engine."
###
This research was supported by the I-Core Program of the Planning and Budgeting Committee and the Israel Science Foundation, The Ministry of Economy and Industry of Infrastructure Energy and Water, as well as the Adelis Foundation.
####
About American Associates, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
American Associates, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (AABGU) plays a vital role in sustaining David Ben-Gurion's vision: creating a world-class institution of education and research in the Israeli desert, nurturing the Negev community and sharing the University's expertise locally and around the globe. As Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) looks ahead to turning 50 in 2020, AABGU imagines a future that goes beyond the walls of academia. It is a future where BGU invents a new world and inspires a vision for a stronger Israel and its next generation of leaders. Together with supporters, AABGU will help the University foster excellence in teaching, research and outreach to the communities of the Negev for the next 50 years and beyond. Visit vision.aabgu.org to learn more.
AABGU, headquartered in Manhattan, has nine regional offices throughout the United States.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Andrew Lavin
516-944-4486
Copyright © American Associates, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
![]() Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
![]() Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








