Home > Press > Nanotech 'tattoo' can map emotions and monitor muscle activity: Novel skin electrode is comfortable and has endless commercial and medical applications, says Tel Aviv University researcher
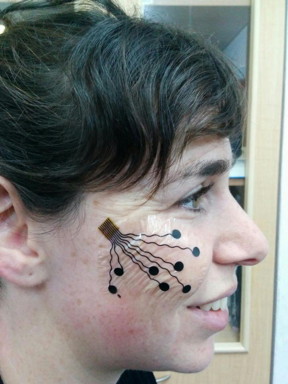 |
| A nanotech "tattoo" was developed by Tel Aviv University. CREDIT: American Friends of Tel Aviv University (AFTAU) |
Abstract:
A new temporary "electronic tattoo" developed by Tel Aviv University that can measure the activity of muscle and nerve cells researchers is poised to revolutionize medicine, rehabilitation, and even business and marketing research.
Nanotech 'tattoo' can map emotions and monitor muscle activity: Novel skin electrode is comfortable and has endless commercial and medical applications, says Tel Aviv University researcher
New York, NY | Posted on July 12th, 2016The tattoo consists of a carbon electrode, an adhesive surface that attaches to the skin, and a nanotechnology-based conductive polymer coating that enhances the electrode's performance. It records a strong, steady signal for hours on end without irritating the skin.
The electrode, developed by Prof. Yael Hanein, head of TAU's Center for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, may improve the therapeutic restoration of damaged nerves and tissue -- and may even lead to new insights into our emotional life.
Prof. Hanein's research was published last month in Scientific Reports and presented at an international nanomedicine program held at TAU.
"Stick it on and forget about it"
One major application of the new electrode is the mapping of emotion by monitoring facial expressions through electric signals received from facial muscles. "The ability to identify and map people's emotions has many potential uses," said Prof. Hanein. "Advertisers, pollsters, media professionals, and others -- all want to test people's reactions to various products and situations. Today, with no accurate scientific tools available, they rely mostly on inevitably subjective questionnaires.
"Researchers worldwide are trying to develop methods for mapping emotions by analyzing facial expressions, mostly via photos and smart software," Prof. Hanein continued. "But our skin electrode provides a more direct and convenient solution."
The device was first developed as an alternative to electromyography, a test that assesses the health of muscles and nerve cells. It's an uncomfortable and unpleasant medical procedure that requires patients to lie sedentary in the lab for hours on end. Often a needle is stuck into muscle tissue to record its electrical activity, or patients are swabbed with a cold, sticky gel and attached to unwieldy surface electrodes.
"Our tattoo permits patients to carry on with their daily routines, while the electrode monitors their muscle and nerve activity," said Prof. Hanein. "The idea is: stick it on and forget about it."
Applications for rehabilitation and more
According to Prof. Hanein, the new skin electrode has other important therapeutic applications. The tattoo will be used to monitor the muscle activity of patients with neurodegenerative diseases in a study at Tel Aviv Medical Center.
"But that's not all," said Prof. Hanein. "The physiological data measured in specific muscles may be used in the future to indicate the alertness of drivers on the road; patients in rehabilitation following stroke or brain injury may utilize the 'tattoo' to improve muscle control; and amputees may employ it to move artificial limbs with remaining muscles."
The electrode is the product of a European Research Council (ERC) project and received support from the BSMT Consortium of Israel's Ministry of Economy.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
George Hunka
212-742-9070
Copyright © American Friends of Tel Aviv University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








