Home > Press > Advanced energy storage material gets unprecedented nanoscale analysis
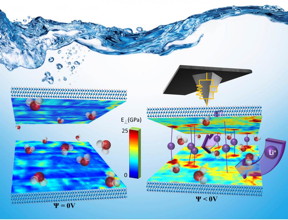 |
| When a negative bias is applied to a two-dimensional MXene electrode, Li+ ions from the electrolyte migrate in the material via specific channels to the reaction sites, where the electron transfer occurs. Scanning probe microscopy at Oak Ridge National Laboratory has provided the first nanoscale, liquid environment analysis of this energy storage material. CREDIT: ORNL |
Abstract:
Researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory have combined advanced in-situ microscopy and theoretical calculations to uncover important clues to the properties of a promising next-generation energy storage material for supercapacitors and batteries.
Advanced energy storage material gets unprecedented nanoscale analysis
Oak Ridge, TN | Posted on March 17th, 2016ORNL's Fluid Interface Reactions, Structures and Transport (FIRST) research team, using scanning probe microscopy made available through the Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences (CNMS) user program, have observed for the first time at the nanoscale and in a liquid environment how ions move and diffuse between layers of a two-dimensional electrode during electrochemical cycling. This migration is critical to understanding how energy is stored in the material, called MXene, and what drives its exceptional energy storage properties.
"We have developed a technique for liquid environments that allows us to track how ions enter the interlayer spaces. There is very little information on how this actually happens," said Nina Balke, one of a team of researchers working with Drexel University's Yury Gogotsi in the FIRST Center, a DOE Office of Science Energy Frontier Research Center.
"The energy storage properties have been characterized on a microscopic scale, but no one knows what happens in the active material on the nanoscale in terms of ion insertion and how this affects stresses and strains in the material," Balke said.
The so-called MXene material -- which acts as a two-dimensional electrode that could be fabricated with the flexibility of a sheet of paper -- is based on MAX-phase ceramics, which have been studied for decades. Chemical removal of the "A" layer leaves two-dimensional flakes composed of transition metal layers -- the "M" -- sandwiching carbon or nitrogen layers (the "X") in the resulting MXene, which physically resembles graphite.
These MXenes, which have exhibited very high capacitance, or ability to store electrical charge, have only recently been explored as an energy storage medium for advanced batteries.
"The interaction and charge transfer of the ion and the MXene layers is very important for its performance as an energy storage medium. The adsorption processes drive interesting phenomena that govern the mechanisms we observed through scanning probe microscopy," said FIRST researcher Jeremy Come.
The researchers explored how the ions enter the material, how they move once inside the materials and how they interact with the active material. For example, if cations, which are positively charged, are introduced into the negatively charged MXene material, the material contracts, becoming stiffer.
That observation laid the groundwork for the scanning probe microscopy-based nanoscale characterization. The researchers measured the local changes in stiffness when ions enter the material. There is a direct correlation with the diffusion pattern of ions and the stiffness of the material.
Come noted that the ions are inserted into the electrode in a solution.
"Therefore, we need to work in liquid environment to drive the ions within the MXene material. Then we can measure the mechanical properties in-situ at different stages of charge storage, which gives us direct insight about where the ions are stored," he said.
Until this study the technique had not been done in a liquid environment.
The processes behind ion insertion and the ionic interactions in the electrode material had been out of reach at the nanoscale until the CNMS scanning probe microscopy group's studies. The experiments underscore the need for in-situ analysis to understand the nanoscale elastic changes in the 2D material in both dry and wet environments and the effect of ion storage on the energy storage material over time.
The researchers' next steps are to improve the ionic diffusion paths in the material and explore different materials from the MXene family. Ultimately, the team hopes to understand the process's fundamental mechanism and mechanical properties, which would allow tuning the energy storage as well as improving the material's performance and lifetime.
ORNL's FIRST research team also provided additional calculations and simulations based on density functional theory that support the experimental findings. The work was recently published in the Journal Advanced Energy Materials.
###
The research team in addition to Balke and Come and Drexel's Gogotsi included Michael Naguib, Stephen Jesse, Sergei V. Kalinin, Paul R.C. Kent and Yu Xie, all of ORNL.
####
About Oak Ridge National Laboratory
The FIRST Center is an Energy Frontier Research Center supported by the DOE Office of Science (Basic Energy Sciences). The Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences and the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center are DOE Office of Science User Facilities.
UT-Battelle manages ORNL for the DOE's Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov/.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Bill Cabage
865-574-4399
Copyright © Oak Ridge National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








