Home > Press > CU-Boulder ultrafast microscope used to make slow-motion electron movie
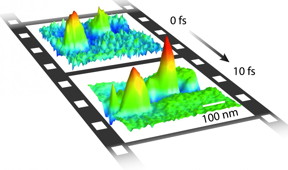 |
| This is an image captured by CU-Boulder researchers using an ultrafast optical microscope shows clouds of electrons oscillating in gold material in space and time. The width of the image is 100 nanometers (about the size of a particle that will fit through a surgical mask), while the time between the top and bottom frame (10 fs, or femtoseconds) is less than 1 trillionth of a second. CREDIT: University of Colorado |
Abstract:
University of Colorado Boulder researchers have demonstrated the use of the world's first ultrafast optical microscope, allowing them to probe and visualize matter at the atomic level with mind-bending speed.
CU-Boulder ultrafast microscope used to make slow-motion electron movie
Boulder, CO | Posted on February 17th, 2016The ultrafast optical microscope assembled by the research team is 1,000 times more powerful than a conventional optical microscope, said CU-Boulder physics Professor Markus Raschke, lead study author. The "image frame" rate, or speed captured by the team, is 1 trillion times faster than the blink of an eye, allowing the researchers to make real-time, slow-motion movies of light interacting with electrons in nanomaterials - in this case a thin gold film.
"This is the first time anyone has been able to probe matter on its natural time and length scale," said Raschke. "We imaged and measured the motions of electrons in real space and time, and we were able to make it into a movie to help us better understand the fundamental physical processes."
A paper on the subject appears in the Feb. 8 issue of Nature Nanotechnology.
Matter is sometimes described as the "stuff of the universe" - the molecules, atoms and charged particles, or ions, that make up everything around us. Matter has several states, most prominently solid, liquid and gas.
According to the CU-Boulder researchers, a number of important processes like photosynthesis, energy conversion and use, and biological functions are based on the transfer of electrons and ions from molecule to molecule. The team used a technique called "plasmonic nanofocusing" to focus extraordinarily short laser pulses into tiny bits of gold film matter using a nanometer-sized metal tip.
"Our study brings nanoscale microscopy to the next level, with the ability to capture detailed images evolving on extremely fast time scales," said Vasily Kravtsov, a CU-Boulder graduate student in physics and first author of the paper.
Other co-authors on the Nature Nanotechnology paper include CU-Boulder postdoctoral researcher Ronald Ulbricht and former CU-Boulder postdoctoral researcher Joanna Atkin, now a faculty member at the University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill.
"This work expands the reach of optical microscopes," said Raschke. "Using this technique, researchers can image the elementary processes in materials ranging from battery electrodes to solar cells, helping to improve their efficiency and lifetime."
Unlike electron microscope approaches, the new technique does not require ultra-high vacuum techniques and is particularly promising for studying ultrafast processes like charge and energy transport in soft matter, including biological materials, said Kravtsov.
###
The study was funded in part by the National Science Foundation with support from the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Markus Rasche
303-492-1366
Jim Scott
CU-Boulder media relations
303-492-3114
Copyright © University of Colorado at Boulder
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








