Home > Press > Collaboration could lead to biodegradable computer chips
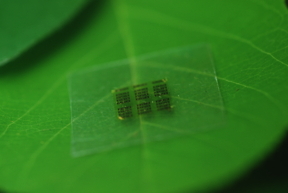 |
| A cellulose nanofibril (CNF) computer chip rests on a leaf. Photo: Yei Hwan Jung, Wisconsin Nano Engineering Device Laboratory. |
Abstract:
Portable electronics - typically made of non-renewable, non-biodegradable and potentially toxic materials - are discarded at an alarming rate in consumers' pursuit of the next best electronic gadget.
Collaboration could lead to biodegradable computer chips
Madison, WI | Posted on May 28th, 2015The research team, led by UW-Madison electrical and computer engineering professor Zhenqiang "Jack" Ma, described the new device in a paper published today (May 26, 2015) by the journal Nature Communications. The paper demonstrates the feasibility of replacing the substrate, or support layer, of a computer chip, with cellulose nanofibril (CNF), a flexible, biodegradable material made from wood.
"The majority of material in a chip is support. We only use less than a couple of micrometers for everything else," Ma says. "Now the chips are so safe you can put them in the forest and fungus will degrade it. They become as safe as fertilizer."
Zhiyong Cai, project leader for an engineering composite science research group at FPL, has been developing sustainable nanomaterials since 2009.
"If you take a big tree and cut it down to the individual fiber, the most common product is paper. The dimension of the fiber is in the micron stage," Cai says. "But what if we could break it down further to the nano scale? At that scale you can make this material, very strong and transparent CNF paper."
Working with Shaoqin "Sarah" Gong, a UW-Madison professor of biomedical engineering, Cai's group addressed two key barriers to using wood-derived materials in an electronics setting: surface smoothness and thermal expansion.
"You don't want it to expand or shrink too much. Wood is a natural hydroscopic material and could attract moisture from the air and expand," Cai says. "With an epoxy coating on the surface of the CNF, we solved both the surface smoothness and the moisture barrier."
Gong and her students also have been studying bio-based polymers for more than a decade. CNF offers many benefits over current chip substrates, she says.
"The advantage of CNF over other polymers is that it's a bio-based material and most other polymers are petroleum-based polymers. Bio-based materials are sustainable, bio-compatible and biodegradable," Gong says. "And, compared to other polymers, CNF actually has a relatively low thermal expansion coefficient."
The group's work also demonstrates a more environmentally friendly process that showed performance similar to existing chips. The majority of today's wireless devices use gallium arsenide-based microwave chips due to their superior high-frequency operation and power handling capabilities. However, gallium arsenide can be environmentally toxic, particularly in the massive quantities of discarded wireless electronics.
Yei Hwan Jung, a graduate student in electrical and computer engineering and a co-author of the paper, says the new process greatly reduces the use of such expensive and potentially toxic material.
"I've made 1,500 gallium arsenide transistors in a 5-by-6 millimeter chip. Typically for a microwave chip that size, there are only eight to 40 transistors. The rest of the area is just wasted," he says. "We take our design and put it on CNF using deterministic assembly technique, then we can put it wherever we want and make a completely functional circuit with performance comparable to existing chips."
While the biodegradability of these materials will have a positive impact on the environment, Ma says the flexibility of the technology can lead to widespread adoption of these electronic chips.
"Mass-producing current semiconductor chips is so cheap, and it may take time for the industry to adapt to our design," he says. "But flexible electronics are the future, and we think we're going to be well ahead of the curve."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Zhenqiang "Jack" Ma
608-261-1095
John Steeno
608-263-5988
Copyright © University of Wisconsin-Madison
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








