Home > Press > One nanoparticle, 6 types of medical imaging: Tomorrow's doctors could use this technology to obtain a super-clear picture of patients' organs and tissues
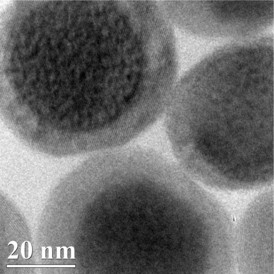 |
| This transmission electron microscopy image shows the nanoparticles, which consist of a core that glows blue when struck by near-infrared light, and an outer fabric of porphyrin-phospholipids (PoP) that wraps around the core.
Credit: Jonathan Lovell |
Abstract:
It's technology so advanced that the machine capable of using it doesn't yet exist.
Using two biocompatible parts, University at Buffalo researchers and their colleagues have designed a nanoparticle that can be detected by six medical imaging techniques:
•computed tomography (CT) scanning;
•positron emission tomography (PET) scanning;
•photoacoustic imaging;
•fluorescence imaging;
•upconversion imaging; and
•Cerenkov luminescence imaging.
One nanoparticle, 6 types of medical imaging: Tomorrow's doctors could use this technology to obtain a super-clear picture of patients' organs and tissues
Buffalo, NY | Posted on January 20th, 2015In the future, patients could receive a single injection of the nanoparticles to have all six types of imaging done.
This kind of "hypermodal" imaging -- if it came to fruition -- would give doctors a much clearer picture of patients' organs and tissues than a single method alone could provide. It could help medical professionals diagnose disease and identify the boundaries of tumors.
"This nanoparticle may open the door for new 'hypermodal' imaging systems that allow a lot of new information to be obtained using just one contrast agent," says researcher Jonathan Lovell, PhD, UB assistant professor of biomedical engineering. "Once such systems are developed, a patient could theoretically go in for one scan with one machine instead of multiple scans with multiple machines."
When Lovell and colleagues used the nanoparticles to examine the lymph nodes of mice, they found that CT and PET scans provided the deepest tissue penetration, while the photoacoustic imaging showed blood vessel details that the first two techniques missed.
Differences like these mean doctors can get a much clearer picture of what's happening inside the body by merging the results of multiple modalities.
A machine capable of performing all six imaging techniques at once has not yet been invented, to Lovell's knowledge, but he and his coauthors hope that discoveries like theirs will spur development of such technology.
The research, Hexamodal Imaging with Porphyrin-Phospholipid-Coated Upconversion Nanoparticles, was published online Jan. 14 in the journal Advanced Materials.
It was led by Lovell; Paras Prasad, PhD, executive director of UB's Institute for Lasers, Photonics and Biophotonics (ILPB); and Guanying Chen, PhD, a researcher at ILPB and Harbin Institute of Technology in China. The team also included additionanl collaborators from these institutions, as well as the University of Wisconsin and POSTECH in South Korea.
The researchers designed the nanoparticles from two components: An "upconversion" core that glows blue when struck by near-infrared light, and an outer fabric of porphyrin-phospholipids (PoP) that wraps around the core.
Each part has unique characteristics that make it ideal for certain types of imaging.
The core, initially designed for upconversion imaging, is made from sodium, ytterbium, fluorine, yttrium and thulium. The ytterbium is dense in electrons -- a property that facilitates detection by CT scans.
The PoP wrapper has biophotonic qualities that make it a great match for fluorescence and photoacoustic imagining. The PoP layer also is adept at attracting copper, which is used in PET and Cerenkov luminescence imaging.
"Combining these two biocompatible components into a single nanoparticle could give tomorrow's doctors a powerful, new tool for medical imaging," says Prasad, also a SUNY Distinguished Professor of chemistry, physics, medicine and electrical engineering at UB. "More studies would have to be done to determine whether the nanoparticle is safe to use for such purposes, but it does not contain toxic metals such as cadmium that are known to pose potential risks and found in some other nanoparticles."
"Another advantage of this core/shell imaging contrast agent is that it could enable biomedical imaging at multiple scales, from single-molecule to cell imaging, as well as from vascular and organ imaging to whole-body bioimaging," Chen adds. "These broad, potential capabilities are due to a plurality of optical, photoacoustic and radionuclide imaging abilities that the agent possesses."
Lovell says the next step in the research is to explore additional uses for the technology.
For example, it might be possible to attach a targeting molecule to the PoP surface that would enable cancer cells to take up the particles, something that photoacoustic and fluorescence imaging can detect due to the properties of the smart PoP coating. This would enable doctors to better see where tumors begin and end, Lovell says.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Charlotte Hsu
716-645-4655
Copyright © University at Buffalo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Cancer
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








