Home > Press > Staying cool in the nanoelectric universe by getting hot: Research hints that nanodevices in microcircuits can protect themselves from heat generation; could boost computing power without large-scale changes to electronics
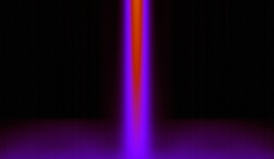 |
| A University at Buffalo study hints that, to make laptops and other portable electronic devices more robust, more heat might be the answer. Here, nanoconductors squeeze an electrical current into a narrow channel, increasing the amount of heat circulating through a microchip’s nanotransistor. Credit: Jon Bird and Jong Han. |
Abstract:
As smartphones, tablets and other gadgets become smaller and more sophisticated, the heat they generate while in use increases. This is a growing problem because it can cause the electronics inside the gadgets to fail.
Staying cool in the nanoelectric universe by getting hot: Research hints that nanodevices in microcircuits can protect themselves from heat generation; could boost computing power without large-scale changes to electronics
Buffalo, NY | Posted on January 23rd, 2014Conventional wisdom suggests the solution is to keep the guts of these gadgets cool.
But a new University at Buffalo research paper hints at the opposite: that is, to make laptops and other portable electronic devices more robust, more heat might be the answer.
"We've found that it's possible to protect nanoelectronic devices from the heat they generate in a way that preserves how these devices function," said Jonathan Bird, UB professor of electrical engineering. "This will hopefully allow us to continue developing more powerful smartphones, tablets and other devices without having a fundamental meltdown in their operation due to overheating."
Bird is the co-lead author along with Jong Han, UB associate professor of physics. Contributing authors are Jebum Lee and Jungwoo Song, who both recently earned PhDs in UB's Department of Electrical Engineering; Shiran Xiao, PhD candidate in electrical engineering at UB; and John L. Reno, Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies at Sandia National Laboratories.
Heat in electronic devices is generated by the movement of electrons through transistors, resistors and other elements of an electrical network. Depending on the network, there are a variety of ways, such as cooling fans and heat sinks, to prevent the circuits from overheating.
But as more integrated circuits and transistors are added to devices to boost their computing power, it's becoming more difficult to keep those elements cool. Most nanoelectrics research centers are working to develop advanced materials that are capable of withstanding the extreme environment inside smartphones, laptops and other devices.
While advanced materials show tremendous potential, the UB research suggests there may still be room within the existing paradigm of electronic devices to continue developing more powerful computers.
To support their findings, the researchers fabricated nanoscale semiconductor devices in a state-of-the-art gallium arsenide crystal provided to UB by Sandia's Reno. The researchers then subjected the chip to a large voltage, squeezing an electrical current through the nanoconductors. This, in turn, increased the amount of heat circulating through the chip's nanotransistor.
But instead of degrading the device, the nanotransistor spontaneously transformed itself into a quantum state that was protected from the effect of heating and provided a robust channel of electric current. To help explain, Bird offered an analogy to Niagara Falls.
"The water, or energy, comes from a source; in this case, the Great Lakes. It's channeled into a narrow point (the Niagara River) and ultimately flows over Niagara Falls. At the bottom of waterfall is dissipated energy. But unlike the waterfall, this dissipated energy recirculates throughout the chip and changes how heat affects, or in this case doesn't affect, the network's operation."
While this behavior may seem unusual, especially conceptualizing it in terms of water flowing over a waterfall, it is the direct result of the quantum mechanical nature of electronics when viewed on the nanoscale. The current is made up of electrons which spontaneously organize to form a narrow conducting filament through the nanoconductor. It is this filament that is so robust against the effects of heating.
"We're not actually eliminating the heat, but we've managed to stop it from affecting the electrical network. In a way, this is an optimization of the current paradigm," said Han, who developed the theoretical models which explain the findings.
The research was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Cory Nealon
Media Relations Manager, Engineering, Libraries, Sustainability
Tel: 716-645-4614
Twitter: @UBengineering
Copyright © University at Buffalo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








