Home > Press > What makes superalloys super - hierarchical microstructure of a superalloy
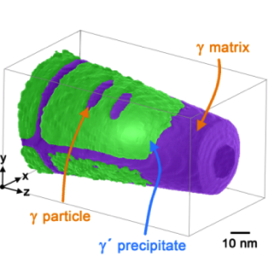 |
| The image shows the three-dimensional reconstruction of an atom probe measurement. The γ matrix (purple) can be seen surrounding the cuboidal γ’ precipitates (green). Only a few nanometre-sized γ platelets can be seen in the γ’ precipitates. Atom probe tomography allows a site specific analysis of the structure at the atomic scale and reveals the chemical composition in measurements of individual areas. Image: HZB |
Abstract:
Researchers have observed for the first time in detail how a hierarchical microstructure develops during heat treatment of a superalloy
What makes superalloys super - hierarchical microstructure of a superalloy
Berlin, Germany | Posted on January 14th, 2014Materials in high-performance turbines have to withstand not only powerful mechanical forces, they also have to maintain their chemical and mechanical properties almost up to their melting points. For this reason, turbine manufacturers have employed special nickel-based high-performance alloys for decades. New work from Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien and Energie (HZB) now shows in detail how new phases in a nickel-based alloy form and evolve, providing clues to how high-performance alloys could be improved. Doctoral student Florian Vogel and Dr. Nelia Wanderka from the HZB Institute of Applied Materials have elegantly combined two methods to accomplish this: transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and atom probe tomography (APT), which they carried out in collaboration with colleagues from the University of Münster.
They were interested in a phase separation phenomenon that has been known for around 50 years, but could neither be precisely observed nor understood until now: The microstructure of nickel-based alloys changes under controlled ageing or heat treatment and in the classical two-phase microstructure new phases are initially formed. Wanderka and Vogel were able to precisely observe the phase separation process on the atomic scale for the first time.
To do so, they simulated the ageing process of the alloy by heat treating it for different periods. They documented how the microstructure changed during the ageing of the alloy using micrographs from the transmission electron microscope. Whereas the classical two-phase microstructure consists of cuboid γ' precipitates embedded in a so called γ-matrix, during heat treatment, spherical γ particles initially form in the γ' precipitates of the alloy, then further coalesce into plates that finally split the γ' precipitates. The thermo-mechanical properties of these types of alloys depend largely on the stability of this γ/γ´ microstructure.
In order to determine the atomic constituents of the individual phases, but primarily to learn about the formation and make-up of the poorly understood γ particle, Vogel and Wanderka investigated the aged samples using atom probe tomography at the University of Münster. They succeeded in reconstructing the atomic lattice of the samples layer by layer and determining the composition of all phases, so that they could explain the chemical evolution of the γ particles.
"Until now, it was assumed that splitting of the γ' precipitates refines the microstructure during ageing, which would be beneficial for the alloy's stability under thermo-mechanical load. We were able to show that this is not correct. The microstructure indeed changes considerably, but it is not improved by the splitting however. We were actually able to correlate the best mechanical properties with the presence of spherical or plate-like γ particles and not with the later stages after splitting of the γ' precipitates has taken place", explains Florian Vogel. Nelia Wanderka adds: "If we want to improve the stability of the microstructure and thus the thermomechanical properties of the alloy, we need to be sure that the γ' precipitates are not split by the γ particles, but instead remain intact through appropriate heat treatment and composition of the alloy. Atom probe tomography helps us in understanding the role of the alloying elements in the formation and growth of the γ particles. From this, we can learn how to influence these processes."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Nelia Wanderka
49-308-062-42079
Florian Vogel
Tel (030) 8062 - 43217
Fax (030) 8062 - 43059
Dr. Antonia Rötger
Tel (030) 8062 - 43733
Fax (030) 8062 - 42998
Copyright © Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








