Home > Press > Measuring flow using a tiny wobbling tube
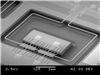 |
| The Coriolis mass flow sensor. The tube is the U-shaped tiny line. In the left lower corner, the electric fingers are visible for measuring the displacement of the tube and activating movement |
Abstract:
One milligram per hour: fluid flow can be measured with great precision using a tiny ‘wobbling' tube with a diameter of only 40 micrometres. Thanks to a new technique, the sensor, which makes use of the ‘Coriolis effect', can be made even more compact, e.g. for medical applications. Scientists at the University of Twente's MESA+ Institute for Nanotechnology have published an article on the subject in Applied Physics Letters.
Measuring flow using a tiny wobbling tube
Enschede, Netherlands | Posted on December 18th, 2012Coriolis meters are often enormous instruments mounted in a pipeline to measure liquid flow accurately. Reduced to micrometre dimensions the result is a sensor that can measure extremely slow-moving small quantities of fluids. The fluid is passed through a tiny rectangular tube that is made to wobble. The Coriolis effect then causes the tube to move upwards as well, and this upward displacement is a measure of the amount of fluid flowing through it.
No magnets
Until now magnets have been used to bring about the wobbling motion. One of the problems was that the magnets are far bigger than the actual sensor. In the Applied Physics Letters article researcher Harmen Droogendijk introduces a new method, known as ‘parametric excitation'. Dozens of ‘electric fingers' attached to the tube fit between identical opposing fingers mounted on supports running
parallel to the tube. The extent to which these opposing sets of fingers slide between one another can be used to measure the tube's lateral displacement. But we could also use them to set the tube in
motion, thought Droogendijk. He found that there is a limited area of electrical tension where the tube moves up and down much more than at a lower or higher tension, though this has to be tuned very precisely. Droogendijk carried out mathematical modelling, resulting in a new design that no longer needs magnets. More research is needed to find out whether the current lower limit of approximately 1 milligram per hour can be lowered even further.
The research was carried out in the Transducers Science and Technology group led by Prof. Gijs Krijnen, which is part of the University of Twente's MESA+ Institute for Nanotechnology. It received financial support from the Dutch national nanotechnology program NanoNed. More research is needed to find
out whether the current lower limit of approximately 1 milligram per hour can be lowered even further.
Industrial applications
The Coriolis mass flow sensor is being further developed by Bronkhorst High-Tech in Ruurlo to produce a precision instrument for such things as monitoring medical IV pumps, analysing medicines using liquid
chromatography, and use in microreactors and the manufacture of solar cells.
Full bibliographic information
The article, ´Parametric excitation of a micro Coriolis mass flow sensor´, by Harmen Droogendijk, Jarno Groenesteijn, Jeroen Haneveld (Micronit Microfluidics), Remco Sanders, Remco Wiegerink, Theo Lammerink, Joost Lötters (Bronkhorst High-Tech) and Gijs Krijnen, has been published in Applied Physics Letters. It is available on request.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Wiebe van der Veen
+31612185692
P.O. Box 217
7500 AE Enschede, Netherlands
053-489 9111
053-489 2000
Copyright © AlphaGalileo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Tools
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








