Home > Press > New optical tweezers trap specimens just a few nanometers across
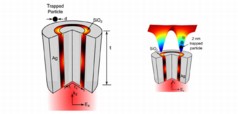 |
| This illustration shows the new aperture design (left) with two layers of silver separated by another of silicon dioxide. The structure focuses light in a novel way to trap particles smaller than ever before. The focused beams are shown in the illustration on the right. |
Abstract:
A microscale technique known as optical trapping uses beams of light as tweezers to hold and manipulate tiny particles. Stanford researchers have found a new way to trap particles smaller than 10 nanometers - and potentially down to just a few atoms in size - which until now have escaped light's grasp.
New optical tweezers trap specimens just a few nanometers across
Stanford, CA | Posted on December 5th, 2012
By Kelly Servick
To grasp and move microscopic objects, such as bacteria and the components of living cells, scientists can harness the power of concentrated light to manipulate them without ever physically touching them.
Now, doctoral student Amr Saleh and Assistant Professor Jennifer Dionne, researchers at the Stanford School of Engineering, have designed an innovative light aperture that allows them to optically trap smaller objects than ever before - potentially just a few atoms in size.
The process of optical trapping - or optical tweezing, as it is often known - involves sculpting a beam of light into a narrow point that produces a strong electromagnetic field. The beam attracts tiny objects and traps them in place, just like a pair of tweezers.
Unfortunately, there are natural limits to the technique. The process breaks down for objects significantly smaller than the wavelength of light. Therefore, optical tweezers cannot grasp super-small objects like individual proteins, which are only a couple of nanometers in diameter.
Saleh and Dionne have shown theoretically that light passed through their novel aperture would stably trap objects as small as 2 nanometers. The design was published in the journal Nano Letters, and Saleh is now building a working prototype of the microscopic device.
Agonies of scale
As a materials scientist, Jennifer Dionne imagined an optical tool that would help her precisely move molecular building blocks into new configurations. "Optical tweezers seemed like a really cool way of assembling new materials," she said. Dionne is the paper's senior author.
Unfortunately, existing optical tweezers are not adept at handling these tiny building blocks. "It's been a known for several decades that trapping nano-sized objects with light would be challenging," said Dionne.
The problem is inherent to the light beam itself. Optical trapping typically uses light in the visible spectrum (with wavelengths between 400 and 700 nanometers) so that scientist can actually see the specimen as they manipulate it.
Due to a physical constraint called the diffraction limit of light, the smallest space in which optical tweezing can trap a particle is approximately half the wavelength of the light beam. In the visible spectrum this would be about 200 nanometers - half the shortest visible wavelength of 400 nanometers.
Thus, if the specimen in question is only 2 nanometers wide - the size of a typical protein - trapping it in a space of 200 nanometers allows only very loose control at best. Scale-wise, it is akin to guiding a minnow with 20-meter-wide fishing net.
Additionally, the optical force that light can exert on an object diminishes as the objects get smaller. "If you want to trap something very small, you need a tremendous amount of power, which will burn your specimen before you can trap it," Saleh said.
Some researchers get around this problem by attaching the specimen to a much larger object that can be dragged around with light. Dionne noted, however, that important molecules like insulin or glucose might behave quite differently when attached to giant anchors than they would on their own. To isolate and move a tiny object without frying it, the researchers needed a way around the limitations of conventional optical trapping.
The promise of plasmonics
Dionne says that the most promising method of moving tiny particles with light relies on plasmonics, a technology that takes advantage of the optical and electronic properties of metals. A strong conductor like silver or gold holds its electrons weakly, giving them freedom to move around near the metal's surface.
When light waves interact with these mobile electrons, they move in what Dionne describes as "a very well-defined, intricate dance," scattering and sculpting the light into electromagnetic waves called plasmon-polaritons. These oscillations have a very short wavelength compared to visible light, enabling them to trap small specimens more tightly.
Dionne and Saleh applied plasmonic principles to design a new aperture that focuses light more effectively. The aperture is structured much like the coaxial cables that transmit television signals, Saleh said. A nanoscale tube of silver is coated in a thin layer of silicon dioxide, and those two layers are wrapped in a second outer layer of silver. When light shines through the silicon dioxide ring, it creates plasmons at the interface where the silver and silicon dioxide meet. The plasmons travel along aperture and emerge on the other end as a powerful, concentrated beam of light.
The Stanford device is not the first plasmonic trap, but it promises to trap the smallest specimens recorded to date. Saleh and Dionne have theoretically shown that their design can trap particles as small as 2 nanometers. With further improvements, their design could even be used to optically trap molecules even smaller.
An optical multi-tool
As nanoscale tools go, this new optical trap would be quite a versatile gadget. While the researchers first envisioned it in the context of materials science, its potential applications span many other fields including biology, pharmacology, and genomics.
Dionne said she would first like to trap a single protein, and try to unravel its twisted structure using visible light alone. Dionne points out that the beam of light could also be used to exert a strong pulling force on stem cells, which has been shown to change how the these important building blocks differentiate into various kinds of cells. Saleh, on the other hand, is particularly excited about moving and stacking tiny particles to explore their attractive forces and create new, "bottom-up" materials and devices.
All this is down the road, however. In the meantime, Saleh is working on turning the design into reality. He hopes to have a prototype by early 2013.
Funding for this research was provided by a Stanford Terman fellowship, an AFOSR Young Investigator Grant and a NSF Career Award.
Kelly Servick is a science-writing intern for the Stanford University School of Engineering.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Andrew Myers
650-736-2245
Copyright © Stanford School of Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Tools
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








