Home > Press > Tracking down smallest biomarkers: PTB and Dectris have developed a vacuum-compatible X-ray detector that allows the size of low-contrast nano-objects to be determined
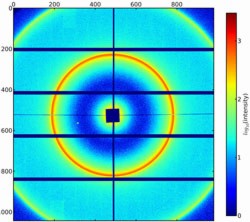 |
| Small-angle X-ray scattering of a micro-vesicle sample (multilamellar liposomes) using the vacuum-compatible Pilatus detector, image recorded at a photon energy of 3 keV. The scattering pattern allows the dimensions of the nano-objects in the examined sample to be determined. (Fig.: PTB) |
Abstract:
Microvesicles are smallest cell elements which are present in all body fluids and are different, depending on whether a person is healthy or sick. This could contribute to detecting numerous diseases, such as, e.g., carcinomas, at an early stage, and to treating them more efficiently. The problem is that the diameter of the relevant microvesicles generally lies below 100 nm, which makes them technically detectable, but their exact size and concentration hardly possible to determine. A new device is now to provide the metrological basis for these promising biomarkers. The vacuum-compatible version of the Pilatus hybrid pixel detector for X-rays, which was developed by Dectris in cooperation with the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB), now allows also the size of nano-particles - which, to date, have been difficult to characterize - to be determined using small-angle X-ray scattering at low photon energies. The detector can also be used for other X-ray-based techniques.
Tracking down smallest biomarkers: PTB and Dectris have developed a vacuum-compatible X-ray detector that allows the size of low-contrast nano-objects to be determined
Braunschweig , Germany | Posted on November 27th, 2012What makes this detector unique is the size of its total surface (17 cm × 18 cm) as well as the fact that it can be operated in vacuum. Operating the detector in vacuum drastically increases the sensitivity of the measuring facility, since the soft X-rays, which are scattered on the sample, are not absorbed by air molecules on their way towards the detector. This device now allows, for example, experiments for size determination of nanoparticles to be carried out with small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) also at the absorption edges of the light elements calcium, sulphur, phosphor or silicon at photon energies below 5 keV with high dynamics and good spatial resolution.
For a few months, the new Pilatus X-ray detector has been used for some of PTB's own research projects. At the synchrotron radiation source BESSY II in Berlin-Adlershof, where PTB has been operating its own laboratory for 15 years, scientists are now using the new detector, for example, to establish the - urgently needed - metrological basis for the size determination of microvesicles. A project carried out within the scope of the European Metrology Research Programme (EMRP) and with the significant participation of the Amsterdam Medical Center in the Netherlands is to contribute decisively to fully exploiting the potential of microvesicles for the early diagnosis of diseases
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michael Krumrey
49-030-348-17110
Copyright © Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() For further information about the detector, please visit:
For further information about the detector, please visit:
![]() For further information about the characterization of microvesicles, please visit:
For further information about the characterization of microvesicles, please visit:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








