Home > Press > Plasmon Bands in Gold-Silver Nanorods
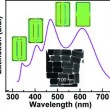 |
| Researchers from The Chinese University of Hong Kong have shown that there are four plasmon bands in (Au core)−(Ag shell) nanorods. |
Abstract:
Localized surface plasmon resonances have recently received intense attention due to their intriguing and complex optical properties. Gold and silver nanostructures, which produce resonances located in the visible range and are stable under ambient conditions, have been studied extensively from fundamental sciences aspects as well as due to their numerous potential applications. Both materials have their advantages. Silver nanocrystals exhibit larger field enhancements, higher refractive index sensitivities, and larger solar energy conversion efficiencies than gold nanocrystals. However, gold nanostructures show tunable longitudinal plasmon wavelengths, are chemically stable and facile growth methods exist. (Gold core) − (silver shell) nanostructures with different shapes have been fabricated to combine these advantages and to allow for tailoring of the plasmon wavelengths by varying the thickness. However, the exact nature of the plasmonic properties of these structures has not been investigated systematically and still remains controversial.
Plasmon Bands in Gold-Silver Nanorods
Germany | Posted on September 20th, 2012Now, Jianfang Wang and co-workers from The Chinese University of Hong Kong have for the first time unraveled the nature of the plasmon bands on gold-silver nanorods. They started with two differently sized gold nanorods and coated them with silver shells with systematically varied thicknesses. The evolution of the plasmon bands, their peak wavelengths and extinction intensities as functions of the shell thickness were studied. The nature of each plasmon band was determined unambiguously with finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) simulations. This first systematical study on the plasmon resonances of gold-silver nanorods will be useful for the construction of optical devices as well as for plasmon-enhanced spectroscopy techniques.
The research was reported in Advanced Optical Materials, a new section in Advanced Materials dedicated to breakthrough discoveries and fundamental research in photonics, plasmonics, metamaterials, and more, covering all aspects of light-matter interactions.
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Wiley-VCH Materials Science Journals
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Link to the original paper on Wiley Online Library:
Link to the original paper on Wiley Online Library:
![]() To get Advanced Optical Materials email alerts click here:
To get Advanced Optical Materials email alerts click here:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








