Home > Press > Nanomaterials: Formation in a flash - A new lithography technique enables the production of nanoscale patterns of titania for high-tech applications
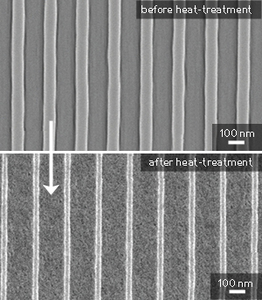 |
| The nanoscale titania pattern before and after heat-treatment. © 2012 American Chemical Society |
Abstract:
Titanium dioxide, or titania, is an inorganic material commonly used as a whitening agent in food and toothpaste. It is also used as one of the main active ingredients in sunscreens. The properties that make titania useful in commercial applications — namely its whitening ability and high refractive index — are now being exploited in a wide range of technological applications.
Nanomaterials: Formation in a flash - A new lithography technique enables the production of nanoscale patterns of titania for high-tech applications
Singapore | Posted on July 6th, 2012One particular area of interest has been the application of titania in dye-sensitized solar cells — devices that can be used to convert sunlight into electricity. Such application often requires the formation of intricate surface patterns, with the key limiting factors for development being cost and speed of processing. Now, Ramakrishnan Ganesan, Mohammad Saifullah and co-workers at the A*STAR Institute of Materials Research and Engineering have described the use of a technique called step-and-flash imprint lithography (SFIL) to produce such patterns on the nanoscale.
"The precursor method to SFIL is thermal nanoimprint lithography, which is extremely time-consuming as it requires temperature-cycling processes to form a pattern," explains Saifullah. "A mold could be pressed into a heated (and softened) resist material or a liquid precursor could be forced into a mold and then hardened upon heating."
Newer processes eliminate the need for heating by using irradiation with ultraviolet (UV) light to harden the polymer. Although this process may be ideal for organic polymer materials, it is more problematic when using inorganic materials such as titania as the liquid precursor materials are highly viscous and do not spread easily. As a result, the dispensing nozzle may sometimes become blocked.
The chemicals used to make titania can also be unstable in solution, so the team had to identify a mixture of components that offered a combination of stability and low viscosity. "We found that an allyl functionalized titanium complex was stable in combination with other polymer precursors," explains Saifullah. The final component of the mixture is a photoinitiator — which starts the polymerization process upon irradiation with UV light.
The mixture was dispensed onto the surface in the form of droplets, and the mold pressed into place to help the liquid spread. Irradiation with UV light results in hardening of the pattern, after which the mold can be removed. A final heating step burns away the organic material, leaving behind a shrunken version of the original pattern made from titania (see image). Significantly, the aspect ratio of the pattern is maintained after the heat-treatment process.
"Our current method is quite specific to titania, but after tackling this most important material, we hope to develop similar procedures for other inorganic materials," says Saifullah.
The A*STAR-affiliated researchers contributing to this research are from the Institute of Materials Research and Engineering
References:
Ganesan, R. et al. Direct patterning of TiO2 using step-and-flash imprint lithography. ACS Nano 6, 1494-1502 (2012). (Direct link to article below)
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
A*STAR Research
Copyright © Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR):
Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR):
![]() Institute of Materials Research and Engineering:
Institute of Materials Research and Engineering:
![]() Link to original article in ACS Nano:
Link to original article in ACS Nano:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Chemistry
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








