Home > Press > Quantum bar magnets in a transparent salt
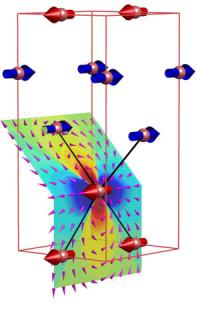 |
| This image shows the antiferromagnetic arrangement of the spins (colored arrows) in the magnetic salt used by the Swiss-German-US-London team.
Credit: University College London |
Abstract:
Scientists have managed to switch on and off the magnetism of a new material using quantum mechanics, making the material a test bed for future quantum devices.
Quantum bar magnets in a transparent salt
London, UK | Posted on June 17th, 2012The international team of researchers led from the Laboratory for Quantum Magnetism (LQM) in Switzerland and the London Centre for Nanotechnology (LCN), found that the material, a transparent salt, did not suffer from the usual complications of other real magnets, and exploited the fact that its quantum spins - which are like tiny atomic magnets - interact according to the rules of large bar magnets. The study is published in Science.
Anybody who has played with toy bar magnets at school will remember that opposite poles attract, lining up parallel to each other when they are placed end to end, and anti-parallel when placed adjacent to each other. As conventional bar magnets are simply too large to reveal any quantum mechanical nature, and most materials are too complex for the spins to interact like true bar magnets, the transparent salt is the perfect material to see what's going on at the quantum level for a dense collection of tiny bar magnets.
The team were able to image all the spins in the special salt, finding that the spins are parallel within pairs of layers, while for adjacent layer pairs, they are antiparallel, as large bar magnets placed adjacent to each other would be. The spin arrangement is called "antiferromagnetic". In contrast, for ferromagnets such as iron, all spins are parallel.
By warming the material to only 0.4 degrees Celsius above the absolute "zero" of temperature where all classical (non-quantum) motion ceases, the team found that the spins lose their order and point in random directions, as iron does when it loses its ferromagnetism when heated to 870 Celsius, much higher than room temperature because of the strong and complex interactions between electron spins in this very common solid.
The team also found that they could achieve the same loss of order by turning on quantum mechanics with an electromagnet containing the salt. Thus, physicists now have a new toy, a collection of tiny bar magnets, which naturally assume an antiferromagnetic configuration and for which they can dial in quantum mechanics at will.
"Understanding and manipulating magnetic properties of more traditional materials such as iron have of course long been key to many familiar technologies, from electric motors to hard drives in digital computers," said Professor Gabriel Aeppli, UCL Director of the LCN.
"While this may seem esoteric, there are deep connections between what has been achieved here and new types of computers, which also rely on the ability to tune quantum mechanics to solve hard problems, like pattern recognition in images."
"Dipolar Antiferromagnetism and Quantum Criticality in LiErF4" is published in the journal [Science] on 15th June 2012 and is embargoed to 14th June 2012. Journalists can obtain copies of the paper by contacting [either the UCL Media Relations Office or Science magazine.
####
About University College London
Founded in 1826, UCL was the first English university established after Oxford and Cambridge, the first to admit students regardless of race, class, religion or gender, and the first to provide systematic teaching of law, architecture and medicine. We are among the world's top universities, as reflected by performance in a range of international rankings and tables. UCL currently has 24,000 students from almost 140 countries, and more than 9,500 employees. Our annual income is over £800 million.
About Laboratory for Quantum Magnetism (LQM):
The Laboratory for Quantum Magnetism (LQM) - headed by Prof. Henrik M. Ronnow, who led the investigation - is part of Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne (EPFL), which is one of the two Swiss Federal Institutes of Technology. With the status of a national school since 1969, this young engineering school on the border of Lake Geneva has grown in many dimensions, to the extent of becoming one of the leading European institutions of science and technology. Its campus brings together over 11,000 students, researchers and staff, and hosts over 350 laboratories and research groups. Websites: www.lqm.epfl.ch and www.epfl.ch
About the London Centre for Nanotechnology:
The London Centre for Nanotechnology is an interdisciplinary joint enterprise between UCL and Imperial College London. In bringing together world-class infrastructure and leading nanotechnology research activities, the Centre has the critical mass to compete with the best facilities world-wide. Research programmes are aligned to three key areas, namely Planet Care, Healthcare and Information Technology and exploit core competencies in the biomedical, physical and engineering sciences. Website: /www.london-nano.com
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Clare Ryan
44-020-310-83846
out of hours +44 (0)7917 271 364
Prof. Henrik M. Ronnow
+41 79 251 7302
or
Prof. Gabriel Aeppli
+44 (0)20 7679 0055 (ext: 30055)
Copyright © University College London
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








