Home > Press > Nanomedicines on their way through the body
 |
Abstract:
Which pathways do nanomedicines take after they have been swallowed? Scientists find a recirculation pathway of polymeric micelles using multimodal nonlinear optical microscopy.
Nanomedicines on their way through the body
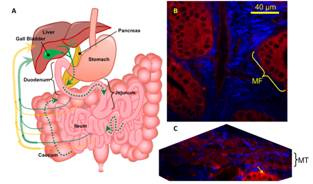
Exeter, UK | Posted on May 25th, 2012Advances in pharmaceutical nanotechnology have yielded ever increasingly sophisticated nanoparticles for medicine delivery. When administered via oral, intravenous, ocular and transcutaneous delivery routes, these nanoparticles can elicit enhanced drug performance. One such recently developed nanoparticle is Quaternary Ammonium Palmitoyl Glycol Chitosan (GCPQ), a chitosan-based polymeric micelle which can be used to encapsulate drugs and enhance their oral absorption and their intravenous activity by up to one order of magnitude. In spite of its great potential, the mechanisms by which GCPQ micelles - or other nanoparticle-based delivery systems - interact with organs at the cellular scale are not yet clear. However, full knowledge of these mechanisms is a prerequisite for a rational design optimizing their performance.
Natalie Laura Garrett an a team of scientist from the University of Exeter and the UCL School of Pharmacy in London (UK) used multimodal nonlinear optical microscopy to investigate these mechanisms using deuterated GCPQ delivered orally to mice.
They combined coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS) microscopy, second harmonic generation (SHG) and two photon fluorescence (TPF) microscopy as a multi-modal label-free method. CARS microscopy has many advantages over conventional imaging including: up to several hundred micron depth penetration into biological tissue; intrinsic optical sectioning and high spatial resolution; label-free chemically specific contrast. When combined with CARS microscopy, TPF and SHG allow detailed three-dimensional visualisation of nanoparticles pinpointed with sub-cellular precision against a complex biological background.
The multi-modal method was used to image three of the most important organs for oral drug delivery: the liver, the intestine and the gall bladder. By doing so, they demonstrated for the first time that orally administered chitosan nanoparticles follow a recirculation pathway from the gastrointestinal tract via enterocytes in the villi, pass into the blood stream and are transported to the hepatocytes and hepatocellular spaces of the liver and then to the gall bladder, before being re-released into the gut together with bile. Such recirculation may also improve drug absorption. (Text by K. Maedefessel-Herrmann)
N.L. Garret et al.; J. Biophotonics 5, 458-568 (2012); DOI 10.1002/jbio. 201200006
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Regina Hagen
Journal Publishing Manager | Editorial Physics Department
Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA
Rotherstr. 21, 10245 Berlin, Germany
Fon: +49 (0) 30/ 47 03 13 21
Fax: +49 (0) 30/ 47 03 13 99
E-Mail:
Copyright © Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Free access to the PDF of the article is available here:
Free access to the PDF of the article is available here:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








