Home > Press > Superconducting strip could become an ultra-low-voltage sensor: Minute-scale interactions govern electronic behaviour of superconductors with potential applications for voltage measurement techniques
 |
Abstract:
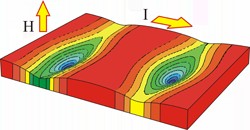
Researchers studying a superconducting strip observed an intermittent motion of magnetic flux which carries vortices inside the regularly spaced weak conducting regions carved into the superconducting material. These vortices resulted in alternating static phases with zero voltage and dynamic phases, which are characterised by non-zero voltage peaks in the superconductor. This study, which is about to be published in EPJ B¹, was carried out by scientists from the Condensed Matter Theory Group of the University of Antwerp, Belgium, working in collaboration with Brazilian colleagues.
Superconducting strip could become an ultra-low-voltage sensor: Minute-scale interactions govern electronic behaviour of superconductors with potential applications for voltage measurement techniques
New York, NY and Heidelberg, Germany | Posted on April 30th, 2012Superconductors, when subjected to sufficiently strong magnetic fields, feature vortices that carry quantized amounts of magnetic flux, although the natural tendency of superconductors is to expel such flux. The authors relied on the Ginzburg-Landau theory to study the dynamic of the nanometric- to millimetric-scale-width superconducting strip, which was subjected to a magnetic field applied at a right angle and a current applied alongside its length.
Typically, weakly acting superconducting regions are natural impediments for the passage of electrical current. However, the authors found that they also work as efficient pathways for vortices to enter and exit the superconducting strip. The increasing magnetic field also increases the density of mutually repelling vortices, which stimulates vortex motion across the strip in the presence of an external current. At the same time, the barrier for vortex entry and exit on the strip boundaries is also dependent on the magnetic field. This interplay of magnetic-field-dependent barriers and vortex-vortex interaction results in an on/off vortex motion in increasing magnetic fields.
Due to the simple geometry of the strip, these results can be confirmed experimentally in magnetoresistance measurements. These findings could be applicable in gate devices used to control various modes of on/off states in electrical systems which operate in specific windows of temperature, applied magnetic field, current and voltage.
Reference:
1. Berdiyorov G. R., de C. Romaguera A. R., Milosevic M. V., Doria M. M., Covaci L., Peeters F. M. (2012), Dynamic and static phases of vortices under an applied drive in a superconducting stripe with an array of weak links, European Physical Journal B (EPJ B), DOI: 10.1140/epjb/e2012-30013-7
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Janine Haubenreisser
Springer
+49-6221-487-8414
Copyright © Springer
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Visit the homepage of the European Physical Journal:
Visit the homepage of the European Physical Journal:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Superconductivity
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








