Home > Press > Slicing mitotic spindle with lasers, nanosurgeons unravel old pole-to-pole theory: Quantitative research shows key organelle of cell division to be more complex than previously thought
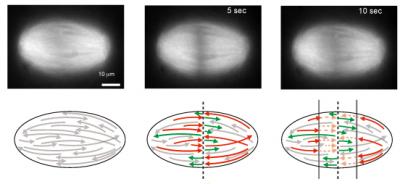 |
| The top shows a series of fluorescent images of a spindle taken before the cut and at 5 seconds and 10 seconds after the cut. Scale bar, 10 µm. The bottom shows a graphical representation of the cut microtubules. The cut generates new 'plus' ends (red) and new 'minus' ends (green). The newly generated minus ends remain stable, whereas the new plus ends depolymerize, which creates two depolymerization fronts of opposed polarity.
Credit: Jan Brugués, Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences. |
Abstract:
The mitotic spindle, an apparatus that segregates chromosomes during cell division, may be more complex than the standard textbook picture suggests, according to researchers at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS).
Slicing mitotic spindle with lasers, nanosurgeons unravel old pole-to-pole theory: Quantitative research shows key organelle of cell division to be more complex than previously thought
Cambridge, MA | Posted on April 26th, 2012The findings, which result from quantitative measurements of the mitotic spindle, will appear tomorrow in the journal Cell.
The researchers used a femtosecond laser to slice through the strands of the organelle and then performed a mathematical analysis to infer the microscopic structure of the spindle from its response to this damage.
"We've been using this nanosurgery technique to understand the architecture and assembly of the spindle in a way that was never possible before," says Eric Mazur, Balkanski Professor of Physics and Applied Physics at Harvard, who co-authored the study. "It's very exciting."
The spindle, which is made of protein strands called microtubules, forms during cell division and segregates chromosomes into the daughter cells. It was previously unclear how microtubules are organized in the spindles of animal cells, and it was often assumed that the microtubules stretch along the length of the entire structure, pole to pole.
Mazur and his colleagues demonstrated that the microtubules can begin to form throughout the spindle. They also vary in length, with the shortest ones close to the poles.
"We wondered whether this size difference might result from a gradient of microtubule stabilization across the spindle, but it actually results from transport," says lead author Jan Brugués, a postdoctoral fellow at SEAS. "The microtubules generally nucleate and grow from the center of the spindle, from which point they are transported towards the poles. They disassemble over the course of their lifespan, resulting in long, young microtubules close to the midline and older, short microtubules closer to the poles."
"This research provides concrete evidence for something that we've only been able to estimate until now," Brugués adds.
Mazur and Brugués worked with Daniel Needleman, Assistant Professor of Applied Physics and Molecular and Cellular Biology at Harvard, and Valeria Nuzzo, a former postdoctoral fellow in Mazur's lab at SEAS, to bring the tools of applied physics to bear on a biological question.
The team used a femtosecond laser to make two small slices perpendicular to the plane of growth of the spindle apparatus in egg extracts of the frog species Xenopus laevis.
They were then able to collect quantitative data on the reconstruction of the spindle following this disruption and precisely determine the length and polarity of individual microtubules. Observing the speed and extent of depolymerization (unraveling) of the spindle, the team worked backwards to compile a complete picture of the beginning and end points of each microtubule. Finally, additional experiments and a numerical model confirmed the role of transport.
"The laser allowed us to make precise cuts and perform experiments that simply were not possible using previous techniques," says Mazur.
With further inquiries into spindle architecture, the researchers hope that scientists will one day have a complete understanding, and possibly even control over, the formation of the spindle.
"Understanding the spindle means understanding cell division," notes Brugués. "With a better understanding of how the spindle is supposed to operate, we have more hope of tackling the range of conditions—from cancer to birth defects—that result from disruptions to the cell cycle or from improper chromosomal segregation."
The research was supported by the National Science Foundation and by a fellowship from the Human Frontiers Science Program.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Caroline Perry
617-496-1351
Copyright © Harvard University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








