Home > Press > Researchers use nanoparticles, magnetic current to damage cancerous cells in mice
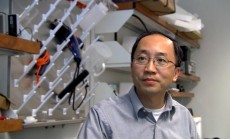 |
| Qun Zhao, assistant professor of physics in the Franklin College of Arts and Sciences, explains his latest research with nanoparticles and hyperthermia cancer treatment. |
Abstract:
Using nanoparticles and alternating magnetic fields, University of Georgia scientists have found that head and neck cancerous tumor cells in mice can be killed in half an hour without harming healthy cells.
Researchers use nanoparticles, magnetic current to damage cancerous cells in mice
Athens, GA | Posted on March 27th, 2012The findings, published recently in the journal Theranostics, mark the first time to the researchers' knowledge this cancer type has been treated using magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle-induced hyperthermia, or above-normal body temperatures, in laboratory mice.
"We show that we can use a small concentration of nanoparticles to kill the cancer cells," said Qun Zhao, lead author and assistant professor of physics in the Franklin College of Arts and Sciences. Researchers found that the treatment easily destroyed the cells of cancerous tumors that were composed entirely of a type of tissue that covers the surface of a body, which is also known as epithelium.
Several researchers around the globe are exploring the use of heated nanoparticles as a potential cancer treatment. Previous studies also have shown that high temperatures created by combining magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with strong alternating magnetic currents can create enough heat to kill tumor cells. Zhao said he is optimistic about his findings, but explained that future studies will need to include larger animals before a human clinical trial could be considered.
For the experiment, researchers injected a tiny amount—a tenth of a teaspoon, or 0.5 milliliter—of nanoparticle solution directly into the tumor site. With the mouse relaxed under anesthesia, they placed the animal in a plastic tube wrapped with a wire coil that generated magnetic fields that alternated directions 100,000 times each second. The magnetic fields produced by the wire coil heated only the concentrated nanoparticles within the cancerous tumor and left the surrounding healthy cells and tissue unharmed.
Zhao said the study paves the way for additional research that might investigate how to use a biodegradable nanoparticle material similar to magnetic iron oxide for other roles in fighting cancer, such as carrying and delivering anti-cancer drugs to the tumor site.
"When the cancer cell is experiencing this heated environment, then it becomes more susceptible to drugs," Zhao said.
Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles could be useful in improving the contrast in magnetic resonance imaging at a cancer site, he said. In other words, the nanoparticles could help physicians detect cancer even if the cancer is not visible to the naked eye with an MRI scan.
"The reason I am interested in using these magnetic nanoparticles is because we hope to one day be able to offer diagnosis and therapeutics, or theranostics, using a single agent," Zhao said.
The research was supported by a National Cancer Institute Head and Neck Specialized Program of Research Excellence at Emory University.
The paper's additional authors are Luning Wang, Rui Cheng, Leidong Mao, Robert Arnold, Simon Platt and Elizabeth W. Howerth, all of UGA, and Zhuo G. Chen of Emory University.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Qun Zhao
706-583-5558
Copyright © University of Georgia
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








