Home > Press > Top journal announces highlighted “hot paper” on AFM-IR research by Anasys scientific advisor, Alexandre Dazzi, and co-workers from the Université de Paris-Sud
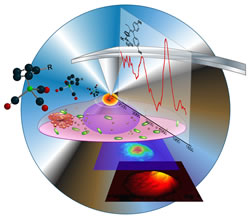 |
| Schematic representation of AFM-IR as described by Dazzi and his colleagues in Angew. Chemie. |
Abstract:
Anasys Instruments is pleased to report the publication and highlighting of a "hot paper" from a group of leading French scientists in the leading scientific journal, Angewandte Chemie. The paper address a molecular mapping challenge using the exciting technique of AFM-IR, the combination of an atomic force microscope (AFM) and IR spectroscopy.
Top journal announces highlighted “hot paper” on AFM-IR research by Anasys scientific advisor, Alexandre Dazzi, and co-workers from the Université de Paris-Sud
Santa Barbara, CA | Posted on May 17th, 2011The mapping of molecules inside cells is a contemporary challenge that requires both high sensitivity and sub-micron resolution. IR-spectroscopy is valuable for chemical imaging. In the case of vibrational excitation in the IR, no photobleaching is induced in contrast to what is observed with organic fluorophores in the visible or UV range. The diffraction limit restricts optical resolution in the IR to over 5 μm. The paper describes how this challenge was overcome using thermal rather than optical detection.
The AFM-IR technique was developed by Dr. Alexandre Dazzi at the University of Paris-Sud. It uses an AFM-tip in contact mode with an object as the IR absorbance detector. This breakthrough technique made it possible for this consortium of chemists, physicists and cell biologists to localize a rhenium-carbonyl complex inside cells after a 1h-incubation at 10 μL. They have also localized the nucleus using its own IR-signature without any trackers and shown that the molecule is localized inside the nucleus.
Dr. Dazzi's research has been at the core of the Anasys nanoIR system. Potential nanoIR application areas include polymer blends, multilayer films and laminates, organic defect analysis, tissue morphology and histology, subcellular spectroscopy, and organic photovoltaics. For further details, please see the application notes at the Anasys website (www.anasysinstruments.com/nano_IR_spectroscopy.php?fi=applications#apn).
Reference: Subcellular Imaging in the mid-IR of a Metal-Carbonyl Moiety using Photothermal Induced Resonance, Clotilde Policar, Jenny-Birgitta Waern, Marie-Aude Plamont, Sylvain Clède, Céline Mayet, Rui Prazeres, Jaan-Michel Ortega, Anne Vessières, Alexandre Dazzi, Angew. Chemie, Int. Ed., 2011, 860.
####
About Anasys Instruments Corporation
Anasys Instruments is dedicated to delivering innovative products and solutions that measure material properties for samples with spatially varying physical and chemical properties at the micro and nanoscale. The Santa Barbara, California-based company has already pioneered two major material property measurement breakthroughs: nanoscale IR Spectroscopy and nanoscale thermal analysis.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Anasys Instruments Corporation
121 Gray Avenue, Suite 100
Santa Barbara, CA 93101
USA
T +1 (805) 730 3310
F +1 (805) 730 3300
www.anasysinstruments.com
NetDyaLog Limited
39 de Bohun Court
Saffron Walden
Essex CB10 2BA
T +44 (0) 1799 521881
www.netdyalog.com
Copyright © Anasys Instruments Corporation
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








