Home > Press > NIST Researchers Create 'Quantum Cats' Made of Light
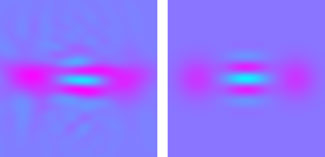 |
| These colorized plots of electric field values indicate how closely the NIST "quantum cats" (left) compare with theoretical predictions for a cat state (right). The purple spots and alternating blue contrast regions in the center of the images indicate the light is in the appropriate quantum state. Credit: Gerrits/NIST |
Abstract:
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have created "quantum cats" made of photons (particles of light), boosting prospects for manipulating light in new ways to enhance precision measurements as well as computing and communications based on quantum physics.
NIST Researchers Create 'Quantum Cats' Made of Light
Gaithersburg, MD | Posted on September 3rd, 2010The NIST experiments, described in a forthcoming paper,* repeatedly produced light pulses that each possessed two exactly opposite properties—specifically, opposite phases, as if the peaks of the light waves were superimposed on the troughs. Physicists call this an optical Schrödinger's cat. NIST's quantum cat is the first to be made by detecting three photons at once and is one of the largest and most well-defined cat states ever made from light. (Larger cat states have been created in different systems by other research groups, including one at NIST.)
A "cat state" is a curiosity of the quantum world, where particles can exist in "superpositions" of two opposite properties simultaneously. Cat state is a reference to German physicist Erwin Schrödinger's famed 1935 theoretical notion of a cat that is both alive and dead simultaneously.
"This is a new state of light, predicted in quantum optics for a long time," says NIST research associate Thomas Gerrits, lead author of the paper. "The technologies that enable us to get these really good results are ultrafast lasers, knowledge of the type of light needed to create the cat state, and photon detectors that can actually count individual photons."
The NIST team created their optical cat state by using an ultrafast laser pulse to excite special crystals to create a form of light known as a squeezed vacuum, which contains only even numbers of photons. A specific number of photons were subtracted from the squeezed vacuum using a device called a beam splitter. The photons were identified with a NIST sensor that efficiently detects and counts individual photons (see "NIST Detector Counts Photons With 99 Percent Efficiency," NIST Tech Beat, Apr. 13, 2010, at www.nist.gov/eeel/optoelectronics/detector_041310.cfm.) Depending on the number of subtracted photons, the remaining light is in a state that is a good approximation of a quantum cat says Gerrits—the best that can be achieved because nobody has been able to create a "real" one, by, for instance, the quantum equivalent to superimposing two weak laser beams with opposite phases.
NIST conducts research on novel states of light because they may enhance measurement techniques such as interferometry, used to measure distance based on the interference of two light beams. The research also may contribute to quantum computing—which may someday solve some problems that are intractable today—and quantum communications, the most secure method known for protecting the privacy of a communications channel. Larger quantum cats of light are needed for accurate information processing.
* T. Gerrits, S. Glancy, T. Clement , B. Calkins, A. Lita, A. Miller, A. Migdall, S.W. Nam, R. Mirin and E. Knill. Generation of optical coherent state superpositions by number-resolved photon subtraction from squeezed vacuum. Physical Review A. Forthcoming.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Laura Ost
303-497-4880
Copyright © NIST
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








