Home > Press > Plastic electronics could slash the cost of solar panels
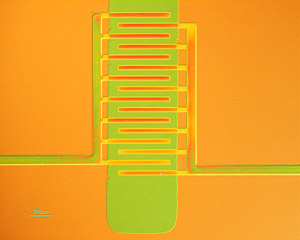 |
| Princeton researchers have developed a new way to manufacture electronic devices made of plastic, employing a process that allows the materials to be formed into useful shapes while maintaining their ability to conduct electricity. In the plastic transistor pictured here, the plastic is molded into interdigitated electrodes (orange) allowing current flow to and from the active channel (green). Image: Loo Research Group |
Abstract:
A new technique developed by Princeton University engineers for producing electricity-conducting plastics could dramatically lower the cost of manufacturing solar panels.
By Chris Emery
Plastic electronics could slash the cost of solar panels
Princeton, NJ | Posted on April 2nd, 2010By overcoming technical hurdles to producing plastics that are translucent, malleable and able to conduct electricity, the researchers have opened the door to broader use of the materials in a wide range of electrical devices.
With mounting concerns about global warming and energy demand, plastics could represent a low-cost alternative to indium tin oxide (ITO), an expensive conducting material currently used in solar panels, according to the researchers.
"Conductive polymers [plastics] have been around for a long time, but processing them to make something useful degraded their ability to conduct electricity," said Yueh-Lin Loo, an associate professor of chemical engineering, who led the Princeton team. "We have figured out how to avoid this trade-off. We can shape the plastics into a useful form while maintaining high conductivity."
A multi-institutional team reported on its new technique in a paper published online March 8 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The area of research, known as "organic electronics" because plastics are carbon-based like living creatures, holds promise for producing new types of electronic devices and new ways of manufacturing existing technologies, but has been hampered by the mysterious loss of conductivity associated with moldable plastics.
"People didn't understand what was happening," said Loo, who co-wrote the paper. "We discovered that in making the polymers moldable, their structures are trapped in a rigid form, which prevented electrical current from traveling through them."
Once they understood the underlying problem, Loo and her colleagues developed a way to relax the structure of the plastics by treating them with an acid after they were processed into the desired form.
Using the method, they were able to make a plastic transistor, a fundamental component of electronics that is used to amplify and switch electronic signals. They produced the electrodes of the transistor by printing the plastic onto a surface, a fast and cheap method similar to the way an ink-jet printer produces a pattern on a piece of paper.
Loo said the technique potentially could be scaled up for mass production presses akin to those used to print newspapers. "Being able to essentially paint on electronics is a big deal," Loo said. "You could distribute the plastics in cartridges the way printer ink is sold, and you wouldn't need exotic machines to print the patterns."
By allowing plastic solar cells to be manufactured using low-cost printing techniques and by replacing ITO as the primary conducting material, the plastics the team developed hold potential for lowering the cost of solar panels.
Currently, the electricity generated by plastic solar cells is collected by a transparent metal conductor made of ITO. The conductor must be transparent so that sunlight can pass through it to the materials in solar cells that absorb the light energy.
A rare and pricey byproduct of mining, ITO had come under increasing demand for use in flat-screen televisions, mobile phones and other devices with display screens. "The cost of indium tin oxide is skyrocketing," Loo said. "To bring down the costs of plastic solar cells, we need to find a replacement for ITO. Our conducting plastics allow sunlight to pass through them, making them a viable alternative."
The researchers anticipate that the plastics also could replace expensive metals used in other electronic devices, such as flexible displays. In addition, the scientists are beginning to explore the use of the plastics in biomedical sensors that would display a certain color if a person had an infection. For instance, the plastics turn from yellow to green when exposed to nitric oxide, a chemical compound produced during ear infections in children.
If the devices could be produced at a low cost, they might be useful in developing countries that lack advanced medical facilities. "You wouldn't need any fancy machines or lab equipment to diagnose an infection," Loo said, "all you would need is your eyes to see the color change in the plastics."
The co-authors of the paper were Joung Eun Yoo, who received her doctorate in chemical engineering from the University of Texas-Austin in 2009 with Loo as her adviser; Kimberly Baldwin, a high school student who spent a summer in Loo's lab; Jacob Tarver, a Princeton chemical engineering graduate student; Enrique Gomez of Pennsylvania State University; Kwang Seok Lee and Yangming Sun of the University of Texas-Austin; Andres Garcia and Thuc-Quyen Nguyen of the University of California-Santa Barbara; and Hong Meng of DuPont Central Research and Development.
The research was supported by the National Science Foundation, the W.M. Keck Foundation and the Arnold and Mabel Beckman Foundation.
####
About Princeton University
Princeton University is a vibrant community of scholarship and learning that stands in the nation's service and in the service of all nations. Chartered in 1746, Princeton is the fourth-oldest college in the United States. Princeton is an independent, coeducational, nondenominational institution that provides undergraduate and graduate instruction in the humanities, social sciences, natural sciences and engineering.
As a world-renowned research university, Princeton seeks to achieve the highest levels of distinction in the discovery and transmission of knowledge and understanding. At the same time, Princeton is distinctive among research universities in its commitment to undergraduate teaching.
Today, more than 1,100 faculty members instruct approximately 5,000 undergraduate students and 2,500 graduate students. The University's generous financial aid program ensures that talented students from all economic backgrounds can afford a Princeton education.
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Princeton University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








