Home > Press > Scientists Use Nanosensors for First Time to Measure Cancer Biomarkers in Blood
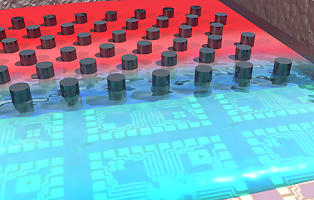 |
| Blood is filtered and transferred to nanosensors on a chip, which can detect and measure cancer biomarkers. (Photo: Mark Reed) |
Abstract:
A team led by Yale University researchers has used nanosensors to measure cancer biomarkers in whole blood for the first time. Their findings, which appear December 13 in the advanced online publication of Nature Nanotechnology, could dramatically simplify the way physicians test for biomarkers of cancer and other diseases.
Scientists Use Nanosensors for First Time to Measure Cancer Biomarkers in Blood
New Haven, CT | Posted on December 14th, 2009The team—led by Mark Reed, Yale's Harold Hodgkinson Professor of Engineering & Applied Science, and Tarek Fahmy, an associate professor of biomedical and chemical engineering—used nanowire sensors to detect and measure concentrations of two specific biomarkers: one for prostate cancer and the other for breast cancer.
"Nanosensors have been around for the past decade, but they only worked in controlled, laboratory settings," Reed said. "This is the first time we've been able to use them with whole blood, which is a complicated solution containing proteins and ions and other things that affect detection."
To overcome the challenge of whole blood detection, the researchers developed a novel device that acts as a filter, catching the biomarkers—in this case, antigens specific to prostate and breast cancer—on a chip while washing away the rest of the blood. Creating a buildup of the antigens on the chip allows for detection down to extremely small concentrations, on the order of picograms per milliliter, with 10 percent accuracy. This is the equivalent of being able to detect the concentration of a single grain of salt dissolved in a large swimming pool.
Until now, detection methods have only been able to determine whether or not a certain biomarker is present in the blood at sufficiently high concentrations for the detection equipment to give reliable estimates of its presence. "This new method is much more precise in reading out concentrations, and is much less dependent on the individual operator's interpretation," Fahmy said.
In addition to relying on somewhat subjective interpretations, current tests are also labor intensive. They involve taking a blood sample, sending it to a lab, using a centrifuge to separate the different components, isolating the plasma and putting it through an hours-long chemical analysis. The whole process takes several days. In comparison, the new device is able to read out biomarker concentrations in a just a few minutes.
"Doctors could have these small, portable devices in their offices and get nearly instant readings," Fahmy said. "They could also carry them into the field and test patients on site."
The new device could also be used to test for a wide range of biomarkers at the same time, from ovarian cancer to cardiovascular disease, Reed said. "The advantage of this technology is that it takes the same effort to make a million devices as it does to make just one. We've brought the power of modern microelectronics to cancer detection."
Authors of the paper include Eric Stern, Aleksandar Vacic, Nitin Rajan, Jason Criscione, Jason Park, Mark Reed and Tarek Fahmy (all of Yale University); Bojan Ilic (Cornell University); David Mooney (Harvard University).
Citation: 10.1038/NNANO.2009.353
####
About Yale University
Yale University comprises three major academic components: Yale College (the undergraduate program), the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, and the professional schools. In addition, Yale encompasses a wide array of centers and programs, libraries, museums, and administrative support offices. Approximately 11,250 students attend Yale.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Press Contact
Suzanne Taylor Muzzin
203-432-8555
Copyright © Yale University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








