Home > Press > Nanobiotech Researcher Receives State Funds to Support Commercialization of diabetes treatment
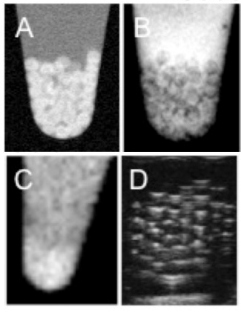 |
| Microcapsules with embedded gadolium-gold nanoparticles can be easily visualized with A (T1-weighted positive contrast MR imaging), B (T2-weighted negative contrast MR imaging). C (X-ray/CT imaging) or D (ultrasound imaging). (Credit: Dian Arifin/Bulte Lab) |
Abstract:
On June 4, the state announced 12 winning research projects that will receive part of $3 million in nanobiotechnology research funding from the 2009 Maryland Nanobiotechnology Research and Industry Competition Grants. Jeff Bulte, an affiliated faculty member of the Institute for NanoBioTechnology and professor of Radiology in the School of Medicine, received a one-time $230,000 to commercialize a promising therapy for type 1 diabetes.
Nanobiotech Researcher Receives State Funds to Support Commercialization of diabetes treatment
Baltimore, MD | Posted on June 24th, 2009Bulte and his postdoctoral fellow Dian Arifin are collaborating with the Baltimore-based company Surgivison Inc. on a project entitled Image-Guided Encapsulated Cell Therapy using Multimodal Nanoparticles. Bulte explains that the project aims to develop microcapsules that contain human islets, the insulin producing cluster of cells in the pancreas, which will be part of a cell therapy for type 1 diabetes. The microcapsules are engineered to protect the islets from attack by the immune system, which would normally treat them as foreign invaders. In addition, the transplanted islets microcapsules also have gadolinium-gold nanoparticles embedded in them so that they can be easily seen with non-invasive imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance, X-ray, computerized tomography, or ultrasound.
"The gadolium-gold nanoparticles allow the encapsulated islets to be injected under imaging guidance. That way you can monitor how many microparticles actually make it to the target site and how many capsules rupture and are subsequently rejected by the immune system," says Bulte. "As part of our team, Surgivision Inc. is developing catheters and injection devices that can be used to deliver and detect our encapsulated islets in real-time."
According to a press release from the state Department of Business and Economic Development (DBED), this was Maryland's first nanobiotechnology research grants competition. DBED, through the Maryland Biotechnology Center, and Maryland Technology Development Corporation jointly administered the nanotechnology grant competition. 103 applications were received in response to the competition's solicitation with 43 finalists subject to technical reviews of their research proposals.
Said Gov. Martin O'Malley in the release, "These grants are an important part of our long-term strategy for growing Maryland's bioscience industry, creating jobs, and positioning Maryland as a national leader in bio and life sciences… (They) will provide critical funding to Maryland companies working to develop innovative life saving technologies for the treatment of cancer and diagnosis of infectious diseases."
####
About Johns Hopkins Institute for NanoBioTechnology
The Johns Hopkins Institute for NanoBioTechnology (INBT) at Johns Hopkins University brings together more than 175 researchers from the Bloomberg School of Public Health, Krieger School of Arts and Sciences, School of Medicine, Applied Physics Laboratory, and Whiting School of Engineering to create new knowledge and new technologies at the interface of nanoscience and medicine.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Johns Hopkins Institute for NanoBioTechnology
3400 North Charles Street
Baltimore, MD 21218
Phone: (410) 516-3423
Fax: (410) 516-2355
Copyright © Johns Hopkins Institute for NanoBioTechnology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








