Home > Press > Nanoscopic probes can track down and attack cancer cells
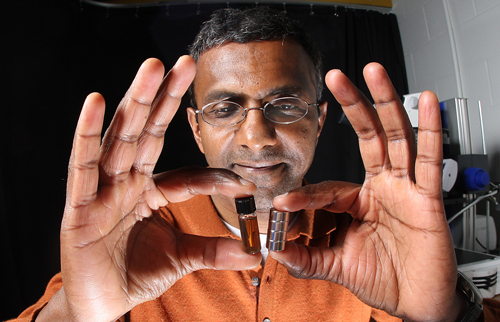 |
| Purdue professor Joseph Irudayaraj uses a magnet to attract tiny magnetic particles in a solution. Irudayaraj designed nanoprobes with gold and magnetic particles that could be used to deliver drugs directly to cancer cells. (Purdue Agricultural Communication photo/Tom Campbell) |
Abstract:
A researcher has developed probes that can help pinpoint the location of tumors and might one day be able to directly attack cancer cells.
Nanoscopic probes can track down and attack cancer cells
West Lafayette, IN | Posted on March 16th, 2009Joseph Irudayaraj, a Purdue University associate professor of agricultural and biological engineering, developed the nanoscale, multifunctional probes, which have antibodies on board, to search out and attach to cancer cells.
A paper detailing the technology was released last week in the online version of Angewandte Chemie, an international chemistry journal.
"If we have a tumor, these probes should have the ability to latch on to it," Irudayaraj said. "The probe could carry drugs to target, treat as well as reveal cancer cells."
Scientists have developed probes that use gold nanorods or magnetic particles, but Irudayaraj's nanoprobes use both, making them easier to track with different imaging devices as they move toward cancer cells.
The magnetic particles can be traced through the use of an MRI machine, while the gold nanorods are luminescent and can be traced through microscopy, a more sensitive and precise process. Irudayaraj said an MRI is less precise than optical luminescence in tracking the probes, but has the advantage of being able to track them deeper in tissue, expanding the probes' possible applications.
The probes, which are about 1,000 times smaller than the diameter of a human hair, contain the antibody Herceptin, used in treatment of metastatic breast cancer. The probes would be injected into the body through a saline buffering fluid, and the Herceptin would find and attach to protein markers on the surface of cancer cells.
"When the cancer cell expresses a protein marker that is complementary to Herceptin, then it binds to that marker," Irudayaraj said. "We are advancing the technology to add other drugs that can be delivered by the probes."
Irudayaraj said better tracking of the nanoprobes could allow doctors to pinpoint the location of known tumors and better treat the cancer.
The novel probes were tested in cultured cancer cells. Irudayaraj said the next step would be to run a series of tests in mice models to determine the dose and stability of the probes.
The research was funded through a National Institute of Health grant, as well as by the Purdue Research Foundation. Irudayaraj is head of a biological engineering team that includes postdoctoral researcher Chungang Wang and graduate student Jiji Chen.
####
Contacts:
Writer: Brian Wallheimer, (765) 496-2050,
Source: Joseph Irudayaraj, (765) 494-0388,
Ag Communications: (765) 494-2722;
Beth Forbes,
Agriculture News Page
Copyright © Purdue University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Purdue University Agricultural News
Purdue University Agricultural News
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








