Home > Press > ‘Femtomolar Optical Tweezers’ May Enable Sensitive Blood Tests
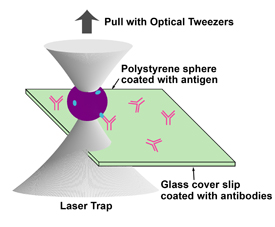 |
| Basic scheme of an optical tweezer-based sensor of biological particles. A microsphere covered with a specific antigen (such as a virus or other infectious agent) is trapped and pulled away from a surface containing the corresponding antibodies. The minimum amount of force applied to the tweezers to break the bonds can provide information on the concentration of antibodies on the surface.
Credit: NIST |
Abstract:
Cutting-edge "tweezers" are so sensitive that they can feel the tell-tale tug of tiny concentrations of pathogens in blood samples, yet don't ever need to be sterilized—or even held—as they are ephemeral and weightless. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has licensed a patented "optical tweezers" technique for detecting and measuring very small concentrations of a biological substance—such as a virus on a surface. NIST has issued a non-exclusive license for the technology to Haemonetics, a global health care company that provides blood management technologies for hospitals and blood and plasma collection agencies.
‘Femtomolar Optical Tweezers’ May Enable Sensitive Blood Tests
GAITHERSBURG, MD | Posted on November 12th, 2008Optical tweezers are actually tightly focused laser beams. They can trap certain objects, such as latex microspheres or biological cells, and move them around in water. This occurs because the lasers' electric fields interact with electric charges on the objects.
To detect disease-causing agents, researchers can coat a microsphere with antibody particles and then touch it to a surface containing infectious particles (antigens). The antigens then stick to the antibodies on the sphere, reminiscent of Velcro, in which loops on one strip combine with hooks on the other. By determining how much laser power is required to pull the microsphere away from the surface, one can then calculate the amount of force needed to break off the antibodies from the antigens and thus count the number of individual antigens that were bound to the sphere. This in turn can detect and count biological antigens at extraordinarily low "femtomolar" concentrations—roughly equivalent to one antigen particle per quadrillion (1,000,000,000,000,000) water molecules.
Following up on earlier work in optical tweezers in the industrial and academic research communities in the 1970s, the licensed technology was patented in 1997 (patent #5,620,857), as a result of research conducted under the NIST BioSensor Consortium. The inventors are Howard Weetall (since retired), Kristian Helmerson, and guest researcher Rani Kishore.
For more information on these or other NIST technologies, should contact Terry Lynch, NIST Office of Technology Partnerships, , (301) 975-2691.
####
About NIST
Founded in 1901, NIST is a non-regulatory federal agency within the U.S. Department of Commerce. NIST's mission is to promote U.S. innovation and industrial competitiveness by advancing measurement science, standards, and technology in ways that enhance economic security and improve our quality of life.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ben Stein
(301) 975-3097
Copyright © NIST
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








