Home > Press > Hansjorg Wyss gives $125 million to create institute for biologically inspired engineering
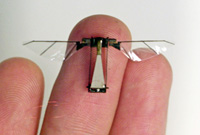 |
| A bioinspired robotic fly fabricated using microengineering.
Images courtesy of Rob Wood |
Abstract:
Engineer, entrepreneur, and philanthropist Hansjörg Wyss MBA '65 has given Harvard University $125 million to create the Hansjörg Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering.
Hansjorg Wyss gives $125 million to create institute for biologically inspired engineering
Cambridge, MA | Posted on October 8th, 2008 Investigators at the Wyss Institute (pronounced "Vees") will strive to uncover the engineering principles that govern living things, and use this knowledge to develop technology solutions for the most pressing healthcare and environmental issues facing humanity. Wyss' gift is the largest individual gift in the University's history.
"I am deeply grateful to Hansjörg Wyss for this gift, which will allow Harvard to make a transformational investment in powerful, collaborative science," said Harvard President and Lincoln Professor of History Drew Faust. "The Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering will form the bedrock for Harvard's emerging efforts in this critical area and will affect research, teaching, and the training of future leaders in this field.
"We regard this gift as an enormous vote of confidence by a donor who is both extraordinarily generous and extraordinarily knowledgeable in this field," Faust continued. "This gift underscores Harvard's ability to lead and to make very significant contributions in a field that is of increasing importance to scientists in a number of areas, and to science more generally."
The Wyss Institute will be a collaborative enterprise bringing together experimentalists, theoreticians, and clinicians with expertise in engineering, biology, chemistry, physics, mathematics, computer science, robotics, medicine, and surgery from Harvard's Schools and affiliated hospitals, as well as from neighboring universities.
The multidisciplinary effort will function as the cornerstone of Harvard's broader efforts in bioengineering, and will build on many elements of the Harvard Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering, which was created with seed support from the Harvard University Science and Engineering Committee in response to a faculty-developed plan for this burgeoning discipline.
Wyss' gift will provide funds for seven endowed faculty positions, as well as major operating funds for the institute. The locus of the Wyss Institute will be in the first science complex currently under construction on Harvard's campus in the Allston neighborhood of Boston.
"I am humbled to have the opportunity to contribute in a meaningful way to efforts that I firmly believe will change the future course of science and medicine," Wyss said. "Little did I dream when I began my career in engineering that we would reach a point where engineers and biologists would be using nature's templates to create solutions to our medical and environmental challenges."
President Faust and Provost Steven E. Hyman, together with Dean Jeffrey Flier, Dean Michael Smith, and former Dean Venkatesh Narayanamurti — of the Harvard Medical School (HMS), Faculty of Arts and Sciences (FAS), and School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), respectively — announced that Donald Ingber, Judah Folkman Professor of Vascular Biology at Harvard Medical School and Children's Hospital Boston, and professor of bioengineering at SEAS, will serve as the Wyss Institute's founding director.
"Hansjörg Wyss' vision for the potential inherent in newly emerging areas of bioengineering will allow Harvard to integrate the worlds of biology and engineering to develop nontraditional solutions to seemingly insurmountable challenges," said Hyman. "Don Ingber's leadership and commitment to exploring these possibilities will make this vision a reality."
Hyman noted that the establishment of the Wyss Institute follows Harvard's "commitment to the overall growth of engineering at Harvard — exemplified by changing the status of the former Division of Engineering to a School of Engineering — but in the context of a liberal arts-focused research institution. With respect to bioengineering in particular, we are at a wonderful intellectual inflection point where we're beginning to see a new generation of bioengineering in which I think no one has an advantage, and where we will provide very substantial intellectual partnerships for such activities as our Stem Cell Institute and for the Systems Biology activities. Those partnerships might, for example," he said, "enable us to convert new basic discoveries into a host of treatments for human beings suffering with illnesses."
In expressing his gratitude to Wyss, Ingber said that "Hansjörg Wyss is a visionary engineer and entrepreneur who understands that transformative change requires risk-taking and breaking down boundaries among existing disciplines. We are indebted to him for his generosity, which will enable engineers, scientists, physicians, and industrial collaborators to work across institutions and disciplines at a level never before possible in an academic setting."
David Mooney, Gordon McKay Professor of Bioengineering at SEAS and co-chair of Harvard's bioengineering working group, said, "I am particularly excited that this gift will allow us to create an interdisciplinary community of scholars who will work together to both develop novel technologies and create a foundation for bioengineering based on a fundamental knowledge of how living systems function."
Purpose and mission
The mission of the Hansjörg Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering is to discover the engineering principles that nature uses to build living things, and to harness these insights to create biologically inspired materials, devices, and control technologies to address unmet medical needs worldwide and bring about a more sustainable world.
Over the past decade in particular, engineering, biology, medicine, and the physical sciences have increasingly converged. Through revolutionary advances in nanotechnology, genetics, and cell engineering, it is now possible to manipulate individual atoms, genes, molecules, and cells one at a time, and to create artificial biological systems. Simultaneous progress in materials science, molecular biology, and tissue engineering has enabled scientists to develop synthetic materials, microdevices, and computational strategies to manipulate cell function, guide tissue formation, and control complex organ physiology. As a result of these developments, the boundary between living and nonliving systems is beginning to break down.
The Wyss Institute will leverage these advances and facilitate new breakthroughs by advancing the science and engineering necessary to develop biomimetic materials, microdevices, microrobots, and innovative disease-reprogramming technologies that emulate how living cells and tissues self-organize and naturally regulate themselves. A deeper understanding of how living systems build, recycle, and control also will ultimately lead to more efficient bioinspired ways of converting energy, controlling manufacturing, improving the environment, and creating a more sustainable world.
Faculty and programs
The Wyss Institute will form a community of engineers, scientists, and clinicians, and provide them with the resources necessary to pursue innovative, multidisciplinary, forward-looking research that will spur the development of transformative new technologies and therapies.
The institute will focus on fundamental, science-driven technology development in the newly emerging fields of synthetic biology, biological control, and living materials.
* The Synthetic Biology Program will develop genetically engineered component parts and circuits necessary to build programmable self-assembling nanomaterials and integrated multifunctional living microdevices.
* The Biological Control Group will devise control strategies that can "reboot" diseased tissues and organs, as well as biologically inspired algorithms for robotic control.
* The Living Materials Program will harness the design principles that govern how living cells, tissues, and organs exhibit their novel material properties and coupled biocatalytic functions, with the goal of fabricating self-organizing biomimetic materials and devices for both medical and nonmedical applications.
The Wyss Institute will also incorporate an Advanced Technology Core, composed of technical experts with extensive expertise in genetic engineering, nanotechnology, microfabrication, materials science, and other critical technologies, who move among different faculty laboratories pursuing problems until they are solved and useful technologies are created. The institute's faculty will translate these new technologies into commercial products and therapies through partnerships with industrial and clinical collaborators. The Wyss Institute also will support clinical faculty researchers who will identify critical clinical challenges, conduct research and development activities necessary to solve these problems, and help to bring these technologies back into the clinic. Such an environment, free of disciplinary boundaries, will foster the training of a new generation of students and fellows who fully understand how to work across disciplines, and how to learn from the power of nature's innovations to advance bioengineering and medicine.
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Harvard University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








