Home > Press > Researchers identify pressure effects on nanomaterials
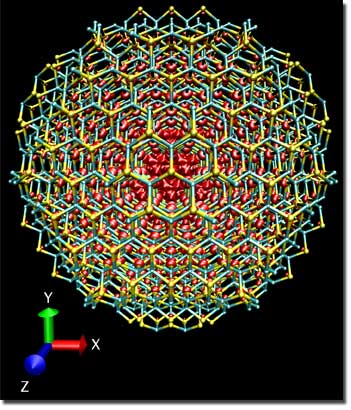 |
| Fluorescence from CdSe quantum dot solids in environments varying from stable to high unstable show that small deviations from uniform stress distribution greatly affect the electronic properties. The blue represents cadmium, the yellow represents selenium and the red represents a cloud of electrons in their excited state. Image by Sebastien Hamel/LLNL |
Abstract:
Transistors, lasers and solar-energy conversion devices may be easier to manipulate because of recent research by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory scientists.
Researchers identify pressure effects on nanomaterials
LIVERMORE, CA | Posted on May 7th, 2008The researchers defined the role high pressure plays in precisely tuning the fundamental properties of nanomaterials and, in particular, nanoparticle assemblies that are important for device applications.
The team, made up of LLNL scientists Christian Grant, Jonathan Crowhurst, Sebastien Hamel, Natalia Zaitseva and former LLNL researcher Andrew Williamson (now at Physic Ventures), subjected quantum dot solids (in this case assemblies of cadmium selenide, or CdSe, nanocrystals) to very high static pressures on the order of 70,000 atmospheres and studied in-situ their response using a laser-based luminescence technique. A quantum dot is a semiconductor whose electrons are confined in all three spatial dimensions.
"We closely compared our results with theoretical calculations," Grant said. "These results were completely consistent with our experimental observations."
But when they applied nonuniform pressure, the results were quite different.
It led to large shifts in the energy associated with the very strong fluorescence of CdSe. CdSe, it was found, is extremely sensitive to the local stress state.
The typical length of quantum dots, which are anywhere in size from one to several hundred nanometers, have chemical and physical properties that are substantially different from those of their bulk and molecular counterparts. (A nanometer is one-billionth of a meter).
Quantum dots can be close-packed into quantum dot solids (QDSs). These nanomaterials can yield insight not only into particle-particle coupling but also tell a story of the evolution of their electronic properties from individual dots and the collective solid.
The Livermore team measured QDSs in several different pressure media, including a liquid and various solid or glassy but still fairly soft media. In addition, they compressed the material directly. Depending on the medium, they observed a steady increase in energy as a function of pressure (uniform pressure case) or after an initial increase, a flattening or even decrease in energy (non-uniform pressure case).
"High pressure provides insight into the fundamental properties of nanoparticles, which can be drastically different from the corresponding bulk material," Grant said.
For example the structural phase transition that occurs in bulk CdSe occurs at much lower pressures than in the case of the QDSs.
The research appears in the June issue of the journal Small.
####
About Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Founded in 1952, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is a national security laboratory, with a mission to ensure national security and apply science and technology to the important issues of our time. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is managed by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Anne M. Stark
Phone: (925) 422-9799
E-mail:
Copyright © Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








