Home > Press > Controlling the speed of enzyme motors brings biomedical applications of nanorobots closer: Recent advances in this field have made micro- and nanomotors promising devices for solving many biomedical problems
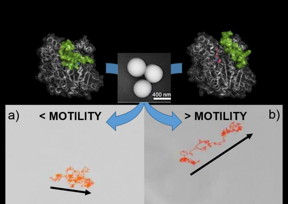 |
| a) Trajectory of an enzyme-powered nanomotor prepared with lipase in a closed conformation and without controlled orientation during immobilization on the silicon nanoparticle surface. b) Trajectory of an enzyme-powered nanomotor prepared with lipase in an open conformation and with controlled orientation during immobilization on the silicon nanoparticle Surface. The central panel shows a scanning electron microscopy image of nanomotors like those used in the experiment. CREDIT CNIC/ IBEC |
Abstract:
A study by scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC), the Universidad Complutense (UCM), Universidad de Girona (UdG), and the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC), working together with other international centers, has overcome one of the key hurdles to the use of nanorobots powered by lipases, enzymes that play essential roles in digestion by breaking down fats in foods so that they can be absorbed.
Controlling the speed of enzyme motors brings biomedical applications of nanorobots closer: Recent advances in this field have made micro- and nanomotors promising devices for solving many biomedical problems
Madrid, Spain | Posted on October 13th, 2020The study was coordinated by Marco Filice of the CNIC Microscopy and Dynamic Imaging Unit--part of the ReDIB Infraestructura Científico Técnica Singular (ICTS)--, professor at Pharmacy Faculty (UCM) and ICREA Research Professor Samuel Sánchez of the IBEC. The article, published in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition, describes a tool for modulating motors powered by enzymes, broadening their potential biomedical and environmental applications.
Microorganisms are able to swim through complex environments, respond to their surroundings, and organize themselves autonomously. Inspired by these abilities, over the past 20 years scientists have managed to artificially replicate these tiny swimmers, first at the macro-micro scale and then at the nano scale, finding applications in environmental remediation and biomedicine.
"The speed, load-bearing capacity, and ease of surface functionalization of micro and nanomotors has seen recent research advances convert these devices into promising instruments for solving many biomedical problems. However, a key challenge to the wider use of these nanorobots is choosing an appropriate motor to propel them," explained Sánchez.
Over the past 5 years, the IBEC group has pioneered the use of enzymes to generate the propulsive force for nanomotors. "Bio-catalytic nanomotors use biological enzymes to convert chemical energy into mechanical force, and this approach has sparked great interest in the field, with urease, catalase, and glucose oxidase among the most frequent choices to power these tiny engines," said Sánchez.
The CNIC group is a leader in the structural manipulation and immobilization of lipase enzymes on the surface of different nanomaterials. Lipases make excellent nanomotor components because their catalytic mechanism involves major conformational changes between an open, active form and a closed,
"In this project, we investigated the effect of modulating the catalytic activity of lipase enzymes to propel silicon-based nanoparticles," explained Filice.
In addition to the 3-dimensional conformation of the enzyme, the team also investigated how controlling the orientation of the enzyme during its immobilization on the nanomotor surface affects its catalytic activity and therefore the propulsion of the nanorobots.
The researchers chemically modified the surface of silicon nanoparticles to generate three specific combinations of lipase conformations and orientations during immobilization: 1) open conformation plus controlled orientation; 2) closed conformation plus uncontrolled orientation; 3) a situation intermediate between 1 and 2.
The team analyzed the three types of nanorobot with spectroscopic techniques, assays to assess catalytic parameters related to enzyme activity, Dynamic Molecular simulations (performed by Professor Silvia Osuna's team at UdG), and direct tracking of individual nanomotor trajectories by microscopy techniques. "The results demonstrate that combining an open enzyme conformation with a specific orientation on the nanomotor is critical to achieving controlled propulsion."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Fátima Lois
34-639-282-477
@CNIC_CARDIO
Copyright © Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
![]() Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
![]() Quantum powers researchers to see the unseen September 8th, 2023
Quantum powers researchers to see the unseen September 8th, 2023
Robotics
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
![]() Kavli Lectures: The art of building small and innovating for industrial impact August 7th, 2020
Kavli Lectures: The art of building small and innovating for industrial impact August 7th, 2020
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








