Home > Press > Nanoscale measurements 100x more precise, thanks to improved two-photon technique
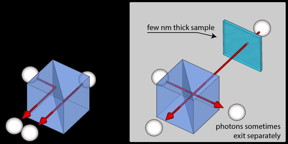 |
| Artist's impression of photons entering beamsplitter, as per the technique. CREDIT University of Warwick |
Abstract:
The precision of measuring nanoscopic structures could be substantially improved, thanks to research involving the University of Warwick and QuantIC researchers at the University of Glasgow and Heriot Watt University into optical sensing.
Nanoscale measurements 100x more precise, thanks to improved two-photon technique
Coventry, UK | Posted on May 8th, 2018Technique uses photons, fundamental components of light, to measure nanoscopic materials thinner than 100,000th the width of a human hair - with 30,000 fired per second and 500bn throughout
Research will mean measurements 100x more precise than existing two-photon techniques - with the potential to aid research into cell membranes and DNA
Two-photon technique more stable than existing one-photon technology
New technique could also be substantially cheaper
The precision of measuring nanoscopic structures could be substantially improved, thanks to research involving the University of Warwick and QuantIC researchers at the University of Glasgow and Heriot Watt University into optical sensing.
QuantIC is the UK Quantum Technology Hub in Quantum Enhanced Imaging and part of the UK National Quantum Technologies Programme.
Using pairs of photons, fundamental components of energy that make up light, the researchers have devised a way to measure the thickness of objects that are less than a 100,000th of the width of a human hair.
The new technique involves firing two near identical photons onto a component known as a beamsplitter, and monitoring their subsequent behaviour - with some 30,000 photons detected per second, and 500bn in use throughout a full experiment.
Because of the tendency of identical photons to 'buddy up' and continue travelling on together -- the result of a delicate quantum interference effect - the researchers' newly developed setup offers the same precision and stability as existing one-photon techniques that, due to the equipment required, are more costly.
Offering a range of potential uses, including research to better understand cell membranes and DNA, as well as quality control for nanoscopic 2D materials of a single atom's thickness, such as graphene, the new research is also a marked improvement on current two-photon techniques with up to 100x better resolution.
To measure the thickness of a transparent object (any object through which a photon is able to pass), each of a pair of identical photons are fired along separate paths:
Photon A then continues into a beamsplitter, whilst Photon B is slowed down by a transparent object before entering the same beamsplitter.
The likelihood that the photons exit the beamsplitter together is then recorded allowing researchers to measure the thickness of the transparent object Photon B passed through.
As the thickness of the sample is increased, the photons are more likely to exit the beamsplitter separately.
Dr George Knee of the University of Warwick's Department of Physics, who developed the theory behind the new method, said:
"What's really exciting about these results is that we can now investigate objects down at the nanoscale with an optical sensor operating on a fundamentally different physical effect.
"Until now, so-called two-photon interference has not been able to achieve such great resolution, meaning that we are stuck with some of the downsides of the established methods based on single-photon interference - which requires more expensive technology than our new two-photon technique.
"We have managed to get a big improvement by tuning the interferometer into a more sensitive operation mode and removing slow drift by repeatedly switching the sample in and out.
"The advantages of being impervious to phase fluctuations and having large dynamic range mean that sensors such as ours could have a big impact on biological imaging and the associated research that it feeds into."
QuantIC co-investigator and lead researcher on the project, Professor Daniele Faccio, whose two photon sensing technology was used to generate the data said:
"The results of our collaboration with the University of Warwick offer a range of potential uses, including research to better understand cell membranes and DNA as well as a quality control for nanoscopic 2D materials of a single atom's thickness, such as graphene.
We are excited to be advancing quantum imaging and helping to maintain the UK's position in the development of new quantum technologies."
The research, Attosecond-Resolution Hong-Ou-Mandel Interferometry, is published by Science Advances.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Luke Walton
782-454-0863
Copyright © University of Warwick
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Nanoelectronics
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
![]() Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








