Home > Press > Characterizing the forces that hold everything together: UMass Amherst physicists offer new open source calculations for molecular interactions
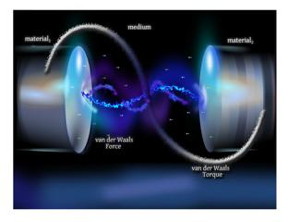 |
| UMass Amherst physicists, with others, provide a new software tool and database to help materials designers with the difficult calculations needed to predict the magnitude of van der Waals interactions between anisotropic or directionally dependent bodies such as those illustrated, with long-range torques. Though small, these forces are dominant on the nanoscale. CREDIT: UMass Amherst |
Abstract:
As electronic, medical and molecular-level biological devices grow smaller and smaller, approaching the nanometer scale, the chemical engineers and materials scientists devising them often struggle to predict the magnitude of molecular interactions on that scale and whether new combinations of materials will assemble and function as designed.
Characterizing the forces that hold everything together: UMass Amherst physicists offer new open source calculations for molecular interactions
Amherst. MA | Posted on September 23rd, 2015This is because the physics of interactions at these scales is difficult, say physicists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, who with colleagues elsewhere this week unveil a project known as Gecko Hamaker, a new computational and modeling software tool plus an open science database to aid those who design nano-scale materials.
In the cover story in today's issue of Langmuir, Adrian Parsegian, Gluckstern Chair in physics, physics doctoral student Jaime Hopkins and adjunct professor Rudolf Podgornik on the UMass Amherst team report calculations of van der Waals interactions between DNA, carbon nanotubes, proteins and various inorganic materials, with colleagues at Case Western Reserve University and the University of Missouri who make up the Gecko-Hamaker project team.
To oversimplify, van der Waals forces are the intermolecular attractions between atoms, molecules, surfaces, that control interactions at the molecular level. The Gecko Hamaker project makes available to its online users a large variety of calculations for nanometer-level interactions that help to predict molecular organization and evaluate whether new combinations of materials will actually stick together and work.
In this work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Parsegian and colleagues say their open-science software opens a whole range of insights into nano-scale interactions that materials scientists haven't been able to access before.
Parsegian explains, "Van der Waals forces are small, but dominant on the nanoscale. We have created a bridge between deep physics and the world of new materials. All miniaturization, all micro- and nano-designs are governed by these forces and interactions, as is behavior of biological macromolecules such as proteins and lipid membranes. These relationships define the stability of materials."
He adds, "People can try putting all kinds of new materials together. This new database and our calculations are going to be important to many different kinds of scientists interested in colloids, biomolecular engineering, those assembling molecular aggregates and working with virus-like nanoparticles, and to people working with membrane stability and stacking. It will be helpful in a broad range of other applications."
Podgornik adds, "They need to know whether different molecules will stick together or not. It's a complicated problem, so they try various tricks and different approaches." One important contribution of Gecko Hamaker is that it includes experimental observations seemingly unrelated to the problem of interactions that help to evaluate the magnitude of van der Waals forces.
Podgornik explains, "Our work is fundamentally different from other approaches, as we don't talk only about forces but also about torques. Our methodology allows us to address orientation, which is more difficult than simply describing van der Waals forces, because you have to add a lot more details to the calculations. It takes much more effort on the fundamental level to add in the orientational degrees of freedom."
He points out that their methods also allow Gecko Hamaker to address non-isotropic, or non-spherical and other complex molecular shapes. "Many molecules don't look like spheres, they look like rods. Certainly in that case, knowing only the forces isn't enough. You must calculate how torque works on orientation. We bring the deeper theory and microscopic understanding to the problem. Van der Waals interactions are known in simple cases, but we've taken on the most difficult ones."
Hopkins, the doctoral student, notes that as an open-science product, Gecko Hamaker's calculations and data are transparent to users, and user feedback improves its quality and ease of use, while also verifying the reproducibility of the science.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Janet Lathrop
413-545-0444
Copyright © University of Massachusetts at Amherst
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Software
![]() Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
![]() Luisier wins SNSF Advanced Grant to develop simulation tools for nanoscale devices July 8th, 2022
Luisier wins SNSF Advanced Grant to develop simulation tools for nanoscale devices July 8th, 2022
![]() Oxford Instruments’ Atomfab® system is production-qualified at a market-leading GaN power electronics device manufacturer December 17th, 2021
Oxford Instruments’ Atomfab® system is production-qualified at a market-leading GaN power electronics device manufacturer December 17th, 2021
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








