Home > Press > 'Giant' charge density disturbances discovered in nanomaterials: Juelich researchers amplify Friedel oscillations in thin metallic films
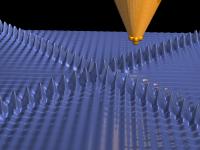 |
| Electron density oscillations on the surface of a metallic film were made visible with the help of low temperature scanning tunneling microscopy.
Credit: Forschungszentrum Jülich |
Abstract:
In metals such as copper or aluminium, so-called conduction electrons are able to move around freely, in the same way as particles in a gas or a liquid. If, however, impurities are implanted into the metal's crystal lattice, the electrons cluster together in a uniform pattern around the point of interference, resembling the ripples that occur when a stone is thrown into a pool of water. Scientists in Jülich have, with the help of computer simulations, now discovered a combination of materials that strengthens these Friedel oscillations and bundles them, as if with a lens, in different directions. With a range of 50 nanometers, these "giant anisotropic charge density oscillations" are many times greater than normal and open up new possibilities in the field of nanoelectronics to exchange or filter magnetic information. (Nature Communications, DOI: 10.1038/ncomms6558)
'Giant' charge density disturbances discovered in nanomaterials: Juelich researchers amplify Friedel oscillations in thin metallic films
Juelich, Germany | Posted on November 26th, 2014The study just published in "Nature Communications" was preceded by an extraordinary discovery: scientists at the Peter Grünberg Institute in Jülich noticed oddly-shaped electron waves in images obtained using scanning tunnelling microscopy. The pictures showed the surface of a thin film of iron with oxygen impurities. "The wave pattern did not consist of closed rings as one would normally expect, but rather spread out crosswise from the point of interference in four different directions", reported Dr. Samir Lounis.
The reason for the unusual distribution of the electron density fluctuations is the virtually square-shaped Fermi surfaces of the material. The electrons with the most energy in an atomic compound are the ones which move about on the Fermi surfaces. The shape of the Fermi surfaces and the mobility of the electrons determine the physical properties of the metals. Fermi surfaces are often circular or square-shaped with rounded edges.
"The virtually flat Fermi surfaces of our samples act as an amplifier for Friedel oscillations, which spread out perpendicular to the surfaces", explains Lounis. The researchers have found out that this effect can be substantially intensified by varying the thickness of the metal. Depending on the number of atomic layers present, piles of Fermi surfaces are formed; the more of them there are, the greater the oscillations. The researchers called this effect the "Giant Anisotropic Charge Density Oscillations".
In principle, the oscillations could be used to exchange information between individual magnetic impurities and further enhance the level of integration of nanoelectronic components. As the oscillations are mainly produced by spins of a single orientation, they could also form the basis for so-called spin filter elements, which are important components in spintronic applications.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Angela Wenzik
49-246-161-6048
Contact:
Dr. Samir Lounis
Quantum Theory of Materials
(PGI-1/IAS-1)
Forschungszentrum Jülich
Phone: +49 24 61 61-6106
Copyright © Forschungszentrum Juelich
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Press release „Nano-Sonar Uses Electrons to Measure under the Surface" 27.2.2009:
Press release „Nano-Sonar Uses Electrons to Measure under the Surface" 27.2.2009:
![]() Institute: "Quantum Theory of Materials" (PGI-1/IAS-1):
Institute: "Quantum Theory of Materials" (PGI-1/IAS-1):
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Thin films
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() Understanding the mechanism of non-uniform formation of diamond film on tools: Paving the way to a dry process with less environmental impact March 24th, 2023
Understanding the mechanism of non-uniform formation of diamond film on tools: Paving the way to a dry process with less environmental impact March 24th, 2023
![]() New study introduces the best graphite films: The work by Distinguished Professor Feng Ding at UNIST has been published in the October 2022 issue of Nature Nanotechnology November 4th, 2022
New study introduces the best graphite films: The work by Distinguished Professor Feng Ding at UNIST has been published in the October 2022 issue of Nature Nanotechnology November 4th, 2022
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
![]() Linearly assembled Ag-Cu nanoclusters: Spin transfer and distance-dependent spin coupling November 4th, 2022
Linearly assembled Ag-Cu nanoclusters: Spin transfer and distance-dependent spin coupling November 4th, 2022
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Memory Technology
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Researchers discover materials exhibiting huge magnetoresistance June 9th, 2023
Researchers discover materials exhibiting huge magnetoresistance June 9th, 2023
Nanoelectronics
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
![]() Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








