Home > Press > Guo Lab Shows Potential of RNA as Heat-resistant Polymer Material for Nanoarchitectures
 |
Abstract:
A team of nanotechnology researchers at the University of Kentucky has discovered new methods to build heat resistant nanostructures and arrays using RNA.
Guo Lab Shows Potential of RNA as Heat-resistant Polymer Material for Nanoarchitectures
Lexington, KY | Posted on April 23rd, 2014The research, led by Peixuan Guo, professor and William Farish Endowed Chair in Nanobiotechnology at the UK College of Pharmacy and Markey Cancer Center, is reported in an article titled "RNA as a Boiling-Resistant Anionic Polymer Material To Build Robust Structures with Defined Shape and Stoichiometry," coauthored by Emil F. Khisamutdinov and Daniel L. Jasinski.
The article, which will appear in a forthcoming edition of the journal ACS Nano, published by the American Chemical Society (ACS), was selected as an ACS "Editors' Choice" and prepublication data is available for free download as a PDF through open access at dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn5006254.
Chemical polymers have seen extensive use in a variety of industries — including clothing, piping, plastics, containers, bottles, cookware, tools and medical materials for drug delivery and tissue engineer materials — because of their high stability and ability to hold their global shape and size. However, on the microscopic scale, these polymers form into random micro-structures, making their size and shape difficult to control.
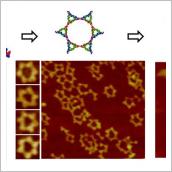
The Guo lab reports that RNA (ribonucleic acid) can be used as an anionic polymer material to build nanostructures with controllable shape and defined structure. The researchers have fabricated a new RNA triangle structure that utilizes RNA's intrinsic control over shape and size on the nano scale, while demonstrating strong stability.
Previously, RNA was seen as structurally fragile and easily dissociable at a range of temperatures from 35-70 degrees Celsius, making its application feasibility in an industrial setting very limited. Using the special RNA motif discovered in Guo's lab and a new methodology, the researchers demonstrated that they can build RNA nanostructures and patterned arrays that are resistant to 100 degrees Celsius, the boiling temperature of water.
The new RNA triangular nanoarchitechtures can be used to form arrays with a controllable repeat number of the scaffold, resembling monomer units in a polymerization reaction. Thus, the Guo lab was able to produce a honeycomb RNA structure with the new RNAs, allowing for the production of RNA sheets.
Experts say this breakthrough pushes the field of RNA nanotechnology forward, positioning RNA to be a new, unique type of polymer with advantages over conventional chemical polymers.
"This research shows great potential for building stable RNA nanoparticles with properties that could be more easily controlled than standard polymers," said Jessica Tucker, National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering program director for drug and gene delivery systems and devices. "The more control we have over the nanoparticles, the better we can tailor them for use in therapeutics for diseases ranging from cancer to diabetes."
The research was supported by National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering AND National Cancer Institute grants NIBIB EB003730 and NCI CA151648.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Keith Hautala
859-323-2396
Copyright © University of Kentucky
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
![]() Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








