Home > Press > Award-winning Microscopic Images: Hidden Beauty of the Nano-cosmos
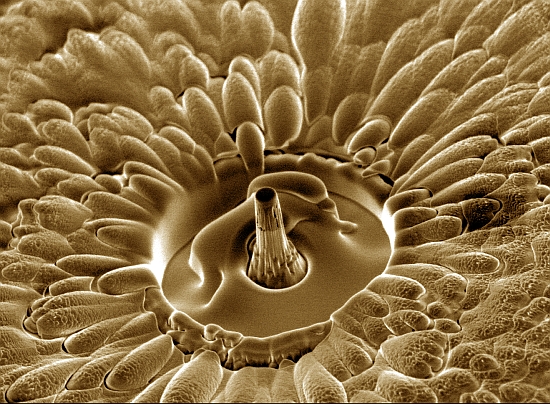 |
| Award-winning image: Many brushes made from carbon nanotubes are formed into a tower 500 nanometres in diameter by using a focused ion beam system. The scanning electron microscope is used to investigate how they behave under the effects of pressure. |
Abstract:
When Empa researchers receive prizes, it is usually to honour their scientific work. However, the photographs from the scanning electron microscope, taken by Siddhartha Pathak during his postdoctoral time at Empa in Thun, have already been recognised several times for their aesthetic value. This was the case again recently, this time at "NanoArt 2011", where he was awarded first prize.
Award-winning Microscopic Images: Hidden Beauty of the Nano-cosmos
Switzerland | Posted on October 12th, 2011It is possible to create real works of art simply from the series of points of an electron microscope image. Siddhartha Pathak proved this more than once during his time as a postdoctoral researcher in Thun. While working in the "Mechanics of Materials and Nanostructures" and "Advanced Materials Processing" laboratories, he frequently invested time creating visually appealing images from the objects of his study.
In his projects in the field of the micromechanics of materials, he pursued the question of how materials from the macro-world behave when they are shrunk to the micro and nanometre scale. Thus, using a focused ion beam system (FIB), he built towers 500 nanometres in diameter from a high-density carpet made of carbon nanotubes. During stress experiments, he wanted to discover at what pressure these buckle. Result: The towers withstand very high loads and are thus suitable candidates for energy-absorbing applications in micromechanical systems.
This resulted in fascinating pictures. It is amazing because an electron microscope first scans over the topographical conditions of nanoscale structures virtually "blindly". From the "sensed" mountains and valleys, maps are then created by stringing together the points. The shapes produced invite "embellishment" with colours. Pathak understood how to conjure up eye-catching and appealing shapes from the black and white images. Johann Michler, Head of the "Mechanics of Materials and Nanostructures" laboratory, said of his former employee: "I think it was his playful instinct and love of unusual ideas that drove him." Pathak also has the necessary sporting spirit to compete with others in this area. For this reason, he liked to take part in competitions where the hidden beauty of the nano-world was the subject.
Pathak and his colleagues have already won five prizes. Only recently, Pathak, who is currently at the "California Institute of Technology" and is researching the microscopic deformation mechanisms of materials for use in space under extreme conditions, managed to win first prize for one of his images in the international online competition "NanoArt21" What remains for science, however, is a different kind of prize, says Michler: "A good cover picture in a professional journal, on the other hand, can still be found in the annals of science for decades." Pathak has also been successful here. In 2010, one of his pictures made it onto the front cover of the professional journal "Materials Today".
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Johann Michler
Mechanics of Materials and Nanostructures
Tel. +41 58 765 62 05
Editorial / Media Contact
Martina Peter
Communications
Tel. +41 58 765 49 87
Copyright © Empa
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
![]() Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
Human Interest/Art
![]() Drawing data in nanometer scale September 30th, 2022
Drawing data in nanometer scale September 30th, 2022
![]() Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
![]() Graphene nanotubes revolutionize touch screen use for prosthetic hands August 3rd, 2021
Graphene nanotubes revolutionize touch screen use for prosthetic hands August 3rd, 2021
![]() JEOL Announces 2020 Microscopy Image Grand Prize Winners January 7th, 2021
JEOL Announces 2020 Microscopy Image Grand Prize Winners January 7th, 2021
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








