Home > Press > New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaks: System could be used aboard underwater vehicles for many applications
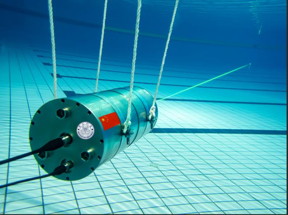 |
| Researchers developed a single-photon Raman lidar system that operates underwater and can remotely distinguish various substances They demonstrated the system by using it to detect varying thicknesses of gasoline oil in a quartz cell that was 12 meters away from the system in a large pool. CREDIT Mingjia Shangguan, Xiamen University |
Abstract:
Researchers report a new single-photon Raman lidar system that operates underwater and can remotely distinguish various substances. They also show that the new system can detect the thickness of the oil underwater up to 12 m away, which could be useful for detecting oil spills.
New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaks: System could be used aboard underwater vehicles for many applications
Washington, DC | Posted on June 30th, 2023“Differentiating substances in water and detecting their distribution characteristics in the ocean are of great significance for marine monitoring and scientific research,” said research team leader Mingjia Shangguan from Xiamen University in China. “For instance, the remote sensing of underwater oil that we demonstrated could be useful for monitoring leaks in underwater oil pipelines.”
Although lidar approaches based on Raman signals have been previously used for detection of underwater substances, existing systems are impractical because they are bulky and require large amounts of power.
In the Optica Publishing Group journal Applied Optics, the researchers describe their new lidar system, which uses just 1 μJ of pulse energy and 22.4 mm of receiver aperture. The entire lidar system is 40 cm long with a diameter of 20 cm and can be operated up to 1 km underwater. To boost sensitivity, the researchers incorporated single-photon detection into their compact underwater Raman lidar system.
“Mounting an underwater Raman lidar system on an autonomous underwater vehicle or remotely operated vehicle could enable monitoring for leaks in underwater oil pipelines,” said Shangguan. “It could potentially also be used to explore oceanic resources or be applied in detecting seafloor sediment types, such as coral reefs.”
Single-photon sensitivity in underwater lidar
Traditional lidar systems designed to operate above water on ships, aircraft or satellites can achieve large-scale ocean profiling, but their detection depth is limited, especially during rough sea conditions. Raman lidar systems, however, can be used for analysis underwater at different depths without being affected by sea conditions.
Raman lidar works by emitting a pulse of green laser light into the water that interacts with substances such as oil. This excites inelastic Raman signals that can be used to identify substances. By measuring the intensity of Raman signals at specific wavelengths, lidar can provide information about the oil content in the water.
“Traditional Raman lidar systems rely on increasing laser power and telescope aperture to achieve remote sensing detection, which leads to a large system size and high-power consumption that make it difficult to integrate lidar systems onto underwater vehicles,” said Shangguan. “The use of single-photon detection technology made this work possible by improving detection sensitivity to the level of single photons.”
The researchers demonstrated their new lidar system by using it to detect varying thicknesses of gasoline oil in a quartz cell that was 12 m away from the system. Both the lidar system and the quartz cell were submerged at a depth of 0.6 m underwater in a large pool. The lidar system was able to detect and distinguish all thicknesses of gasoline, which ranged from 1 mm to 15 mm.
The researchers are now working to increase the number of detection channels and the Raman spectral resolution of the single-photon lidar system to enhance its ability to distinguish different substances in water. This would allow it to be used to analyze underwater bubble types and to detect corals and manganese nodules.
####
About Optica
Optica Publishing Group is a division of Optica (formerly OSA), Advancing Optics and Photonics Worldwide. It publishes the largest collection of peer-reviewed content in optics and photonics, including 18 prestigious journals, the society’s flagship member magazine, and papers from more than 835 conferences, including 6,500+ associated videos. With over 400,000 journal articles, conference papers and videos to search, discover and access, Optica Publishing Group represents the full range of research in the field from around the globe.
About Applied Optics
Applied Optics publishes in-depth peer-reviewed content about applications-centered research in optics. These articles cover research in optical technology, photonics, lasers, information processing, sensing and environmental optics. Applied Optics is published three times per month by Optica Publishing Group and overseen by Editor-in-Chief Gisele Bennett, MEPSS LLC. For more information, visit Applied Optics .
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
Leah Poffenberger
Optica
Office: 2024161994
Expert Contact
Mingjia Shangguan
Xiamen University
Copyright © Optica
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








