Home > Press > Robot caterpillar demonstrates new approach to locomotion for soft robotics
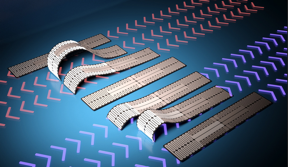 |
| Researchers at North Carolina State University have demonstrated a caterpillar-like soft robot that can move forward, backward and dip under narrow spaces. The caterpillar-bot’s movement is driven by a novel pattern of silver nanowires that use heat to control the way the robot bends, allowing users to steer the robot in either direction. CREDIT Shuang Wu, NC State University |
Abstract:
Researchers at North Carolina State University have demonstrated a caterpillar-like soft robot that can move forward, backward and dip under narrow spaces. The caterpillar-bot’s movement is driven by a novel pattern of silver nanowires that use heat to control the way the robot bends, allowing users to steer the robot in either direction.
Robot caterpillar demonstrates new approach to locomotion for soft robotics
Durham, NC | Posted on March 24th, 2023“A caterpillar’s movement is controlled by local curvature of its body – its body curves differently when it pulls itself forward than it does when it pushes itself backward,” says Yong Zhu, corresponding author of a paper on the work and the Andrew A. Adams Distinguished Professor of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at NC State. “We’ve drawn inspiration from the caterpillar’s biomechanics to mimic that local curvature, and use nanowire heaters to control similar curvature and movement in the caterpillar-bot.
“Engineering soft robots that can move in two different directions is a significant challenge in soft robotics,” Zhu says. “The embedded nanowire heaters allow us to control the movement of the robot in two ways. We can control which sections of the robot bend by controlling the pattern of heating in the soft robot. And we can control the extent to which those sections bend by controlling the amount of heat being applied.”
The caterpillar-bot consists of two layers of polymer, which respond differently when exposed to heat. The bottom layer shrinks, or contracts, when exposed to heat. The top layer expands when exposed to heat. A pattern of silver nanowires is embedded in the expanding layer of polymer. The pattern includes multiple lead points where researchers can apply an electric current. The researchers can control which sections of the nanowire pattern heat up by applying an electric current to different lead points, and can control the amount of heat by applying more or less current.
“We demonstrated that the caterpillar-bot is capable of pulling itself forward and pushing itself backward,” says Shuang Wu, first author of the paper and a postdoctoral researcher at NC State. “In general, the more current we applied, the faster it would move in either direction. However, we found that there was an optimal cycle, which gave the polymer time to cool – effectively allowing the ‘muscle’ to relax before contracting again. If we tried to cycle the caterpillar-bot too quickly, the body did not have time to ‘relax’ before contracting again, which impaired its movement.”
The researchers also demonstrated that the caterpillar-bot’s movement could be controlled to the point where users were able steer it under a very low gap – similar to guiding the robot to slip under a door. In essence, the researchers could control both forward and backward motion as well as how high the robot bent upwards at any point in that process.
“This approach to driving motion in a soft robot is highly energy efficient, and we’re interested in exploring ways that we could make this process even more efficient,” Zhu says. “Additional next steps include integrating this approach to soft robot locomotion with sensors or other technologies for use in various applications – such as search-and-rescue devices.”
The paper, “Caterpillar-Inspired Soft Crawling Robot with Distributed Programmable Thermal Actuation,” will be published March 22 in the journal Science Advances. The paper was co-authored by Jie Yin, an associate professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at NC State; Yaoye Hong, a Ph.D. student at NC State; and by Yao Zhao, a postdoctoral researcher at NC State.
The work was done with support from the National Science Foundation, under grants 2122841, 2005374 and 2126072; and from the National Institutes of Health, under grant number 1R01HD108473.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
Matt Shipman
North Carolina State University
Expert Contact
Yong Zhu
NC State University
Copyright © North Carolina State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Robotics
![]() Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
![]() Femtosecond laser technique births "dancing microrobots": USTC's breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
Femtosecond laser technique births "dancing microrobots": USTC's breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








