Home > Press > Research zeroing in on electronic nose for monitoring air quality, diagnosing disease
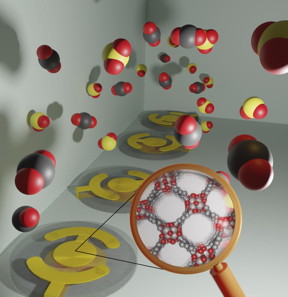 |
| Depiction of a gas sensor array composed of microscale balances coated with thin films of nanoporous materials called metal-organic frameworks. CREDIT Arni Sturluson, Melanie Huynh, OSU College of Engineering |
Abstract:
Research at Oregon State University has pushed science closer to developing an electronic nose for monitoring air quality, detecting safety threats and diagnosing diseases by measuring gases in a patient's breath.
Research zeroing in on electronic nose for monitoring air quality, diagnosing disease
Corvallis, OR | Posted on February 1st, 2020Recently published research led by Cory Simon, assistant professor of chemical engineering in the OSU College of Engineering, in collaboration with chemical engineering professor Chih-Hung Chang focused on materials known as metal-organic frameworks, or MOFs.
The research took aim at a critical yet understudied hurdle in using MOFs as gas sensors: Out of the billions of possible MOFs, how do you determine the right ones for building the optimal electronic nose?
MOFs have nanosized pores and selectively adsorb gases, similar to a sponge. They are ideal for use in sensor arrays because of their tunability, enabling engineers to use a diverse set of materials that allows an array of MOF-based sensors to deliver detailed information.
Depending on which components make up a gas, different amounts of the gas will adsorb in each MOF. That means the composition of a gas can be inferred by measuring the adsorbed gas in the array of MOFs using micro-scale balances.
The challenge is that all MOFs adsorb all gases - not to the same extent, but nevertheless the absence of perfect selectivity prevents an engineer from simply saying, "let's just dedicate this MOF to carbon dioxide, that one to sulfur dioxide, and another one to nitrogen dioxide."
"Curating MOFs for gas sensor arrays is not that simple because each MOF in the array will appreciably adsorb all three of those gases," Simon said.
Human noses navigate this same problem by relying on about 400 different types of olfactory receptors. Much like the MOFs, each olfactory receptor is activated by many different odors, and each odor activates many different receptors; the brain parses the response pattern, allowing people to distinguish a multitude of different odors.
"In our research, we created a mathematical framework that allows us, based on the adsorption properties of MOFs, to decide which combination of MOFs is optimal for a gas sensor array," Simon said. "There will inevitably be some small errors in the measurements of the mass of adsorbed gas, and those errors will corrupt the prediction of the gas composition based on the sensor array response. Our model assesses how well a given combination of MOFs will prevent those small errors from corrupting the estimate of the gas composition."
Though the research was primarily mathematical modeling, the scientists used experimental adsorption data in real MOFs as input, Simon said, adding that Chang is an experimentalist "who we are working with to make a real-life electronic nose to detect air pollutants."
"We are currently seeking external funding together to bring this novel concept into physical realization," Simon said. "Because of this paper, we now have a rational method to computationally design the sensory array, which encompasses simulating gas adsorption in the MOFs with molecular models and simulations to predict their adsorption properties, then using our mathematical method to screen the various combinations of MOFs for the most accurate sensor array."
Meaning that instead of an experimental trial-and-error approach to decide which MOFs to use in a sensor array, engineers can use computational power to curate the best collection of MOFs for an electronic nose.
Another exciting application of such a nose could be diagnosing disease. The volatile organic compounds humans emit, such as through our breath, are filled with biomarkers for multiple diseases, and studies have shown that dogs -- which have twice the number of different olfactory receptors as humans -- can detect diseases with their nose.
Marvelous though they are, however, dogs' noses aren't as practical for widespread diagnostic use as a carefully crafted and manufactured sensor array would be.
###
Findings of the computational MOF research were published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
OSU chemical engineering Ph.D. student Arni Sturluson was the first author on the study. Also collaborating were Ph.D. student Yujing Zhang and undergraduates Rachel Sousa, Melanie Huynh, Caleb Laird, Arthur H.P. York and Carson Silsby.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Cory Simon
541-773-8875
@oregonstatenews
Copyright © Oregon State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Electronic nose
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








