Home > Press > Tiny diamonds could enable huge advances in nanotechnology: UMD researchers develop a new method for pairing nanoscale diamonds with other nanomaterials
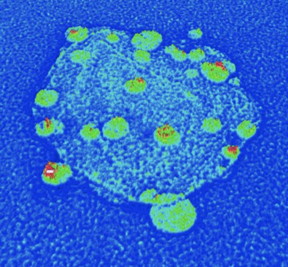 |
| This electron microscope image shows a hybrid nanoparticle consisting of a nanodiamond (roughly 50 nanometers wide) covered in smaller silver nanoparticles that enhance the diamond's optical properties. CREDIT: Min Ouyang |
Abstract:
Nanomaterials have the potential to improve many next-generation technologies. They promise to speed up computer chips, increase the resolution of medical imaging devices and make electronics more energy efficient. But imbuing nanomaterials with the right properties can be time consuming and costly. A new, quick and inexpensive method for constructing diamond-based hybrid nanomaterials could soon launch the field forward.
Tiny diamonds could enable huge advances in nanotechnology: UMD researchers develop a new method for pairing nanoscale diamonds with other nanomaterials
College Park, MD | Posted on June 9th, 2016University of Maryland researchers developed a method to build diamond-based hybrid nanoparticles in large quantities from the ground up, thereby circumventing many of the problems with current methods. The technique is described in the June 8, 2016 issue of the journal Nature Communications.
The process begins with tiny, nanoscale diamonds that contain a specific type of impurity: a single nitrogen atom where a carbon atom should be, with an empty space right next to it, resulting from a second missing carbon atom. This "nitrogen vacancy" impurity gives each diamond special optical and electromagnetic properties.
By attaching other materials to the diamond grains, such as metal particles or semiconducting materials known as "quantum dots," the researchers can create a variety of customizable hybrid nanoparticles, including nanoscale semiconductors and magnets with precisely tailored properties.
"If you pair one of these diamonds with silver or gold nanoparticles, the metal can enhance the nanodiamond's optical properties. If you couple the nanodiamond to a semiconducting quantum dot, the hybrid particle can transfer energy more efficiently," said Min Ouyang, an associate professor of physics at UMD and senior author on the study.
Evidence also suggests that a single nitrogen vacancy exhibits quantum physical properties and could behave as a quantum bit, or qubit, at room temperature, according to Ouyang. Qubits are the functional units of as-yet-elusive quantum computing technology, which may one day revolutionize the way humans store and process information. Nearly all qubits studied to date require ultra-cold temperatures to function properly.
A qubit that works at room temperature would represent a significant step forward, facilitating the integration of quantum circuits into industrial, commercial and consumer-level electronics. The new diamond-hybrid nanomaterials described in Nature Communications hold significant promise for enhancing the performance of nitrogen vacancies when used as qubits, Ouyang noted.
While such applications hold promise for the future, Ouyang and colleagues' main breakthrough is their method for constructing the hybrid nanoparticles. Although other researchers have paired nanodiamonds with complementary nanoparticles, such efforts relied on relatively imprecise methods, such as manually installing the diamonds and particles next to each other onto a larger surface one by one. These methods are costly, time consuming and introduce a host of complications, the researchers say.
"Our key innovation is that we can now reliably and efficiently produce these freestanding hybrid particles in large numbers," explained Ouyang, who also has appointments in the UMD Center for Nanophysics and Advanced Materials and the Maryland NanoCenter, with an affiliate professorship in the UMD Department of Materials Science and Engineering.
The method developed by Ouyang and his colleagues, UMD physics research associate Jianxiao Gong and physics graduate student Nathaniel Steinsultz, also enables precise control of the particles' properties, such as the composition and total number of non-diamond particles. The hybrid nanoparticles could speed the design of room-temperature qubits for quantum computers, brighter dyes for biomedical imaging, and highly sensitive magnetic and temperature sensors, to name a few examples.
"Hybrid materials often have unique properties that arise from interactions between the different components of the hybrid. This is particularly true in nanostructured materials where strong quantum mechanical interactions can occur," said Matthew Doty, an associate professor of materials science and engineering at the University of Delaware who was not involved with the study. "The UMD team's new method creates a unique opportunity for bulk production of tailored hybrid materials. I expect that this advance will enable a number of new approaches for sensing and diagnostic technologies."
The special properties of the nanodiamonds are determined by their nitrogen-vacancies, which cause defects in the diamond's crystal structure. Pure diamonds consist of an orderly lattice of carbon atoms and are completely transparent. However, pure diamonds are quite rare in natural diamond deposits; most have defects resulting from non-carbon impurities such as nitrogen, boron and phosphorus. Such defects create the subtle and desirable color variations seen in gemstone diamonds.
The nanoscale diamonds used in the study were created artificially, and have at least one nitrogen vacancy. This impurity results in an altered bond structure in the otherwise orderly carbon lattice. The altered bond is the source of the optical, electromagnetic and quantum physical properties that make the diamonds useful when paired with other nanomaterials.
Although the current study describes diamonds with nitrogen substitutions, Ouyang points out that the technique can be extended to other diamond impurities as well, each of which could open up new possibilities.
"A major strength of our technique is that it is broadly useful and can be applied to a variety of diamond types and paired with a variety of other nanomaterials," Ouyang explained. "It can also be scaled up fairly easily. We are interested in studying the basic physics further, but also moving toward specific applications. The potential for room-temperature quantum entanglement is particularly exciting and important."
###
The research paper, "Nanodiamond-Based Nanostructures for Coupling Nitrogen-Vacancy Centers to Metal Nanoparticles and Semiconductor Quantum Dots," Jianxiao Gong, Nathaniel Steinsultz and Min Ouyang, was published in the journal Nature Communications on June 8, 2016.
This work was supported by the United States Department of Energy (Award No. DESC0010833), the Office of Naval Research (Award No. N000141410328) and the National Science Foundation (DMR1307800). The content of this article does not necessarily reflect the views of these organizations.
####
About University of Maryland
The College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences at the University of Maryland educates more than 7,000 future scientific leaders in its undergraduate and graduate programs each year. The college's 10 departments and more than a dozen interdisciplinary research centers foster scientific discovery with annual sponsored research funding exceeding $150 million.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matthew Wright
301-405-9267
University of Maryland
College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences
2300 Symons Hall
College Park, MD 20742
http://www.cmns.umd.edu
@UMDscience
Copyright © University of Maryland
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Quantum communication
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Quantum Physics
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








