Home > Press > Valley current control shows way to ultra-low-power devices
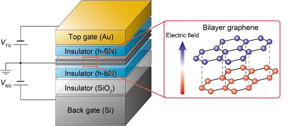 |
| Bilayer graphene is encapsulated on top and bottom by hexagonal boron nitride (an insulator). By applying a voltage to the top and bottom gates it is possible to control the state of the bilayer graphene. Having two gates allows for independent control of the electron density and the vertical electric field. An applied vertical electric field creates a small but significant energy difference between the top and bottom layers of graphene. This difference in energy breaks the symmetry of graphene allowing for the control of valley.
CREDIT: 2015 Seigo Tarucha |
Abstract:
University of Tokyo researchers have demonstrated an electrically-controllable valley current device that may pave the way to ultra-low-power "valleytronics" devices.
Valley current control shows way to ultra-low-power devices
Tokyo, Japan | Posted on November 16th, 2015On the atomic scale, matter behaves as both a particle and a wave. Electrons, therefore, have an associated wavelength that usually can have many different values. In crystalline systems however, certain wavelengths may be favored. Graphene, for example, has two favored wavelengths known as K and K' (K prime). This means that two electrons in graphene can have the same energy but different wavelengths - or, to put it another way, different "valley."
Electronics use charge to represent information, but when charge flows through a material, some energy is dissipated as heat, a problem for all electronic devices in use today. However, if the same quantity of electrons in a channel flow in opposite directions, no net charge is transferred and no heat is dissipated - but in a normal electronic device this would mean that no information was passed either. A valleytronics device transmitting information using pure valley current, where electrons with the same valley flow in one direction, would not have this limitation, and offers a route to realizing extremely low power devices.
Experimental studies on valley current have only recently started. Control of valley current in a graphene monolayer has been demonstrated, but only under very specific conditions and with limited control of conversion from charge current to valley current. In order for valley current to be a viable alternative to charge current-based modern electronics, it is necessary to control the conversion between charge current and valley current over a wide range at high temperatures.
Now, Professor Seigo Tarucha's research group at the Department of Applied Physics at the Graduate School of Engineering has created an electrically controllable valley current device that converts conventional electrical current to valley current, passes it through a long (3.5 micron) channel, then converts the valley current back into charge current that can be detected by a measurable voltage. The research group used a graphene bilayer sandwiched between two insulator layers, with the whole device sandwiched between two conducting layers or 'gates', allowing for the control of valley.
The group transferred valley current over a distance large enough to exclude other possible competing explanations for their results and were able to control the efficiency of valley current conversion over a wide range. The device also operated at temperatures far higher than expected. "We usually measure our devices at temperatures lower than the liquefaction point of Helium (-268.95 C, just 4.2 K above absolute zero) to detect this type of phenomena," says Dr. Yamamoto, a member of the research group. "We were surprised that the signal could be detected even at -203.15 C (70 K). In the future, it may be possible to develop devices that can operate at room temperature."
"Valley current, unlike charge current is non dissipative. This means that no energy is lost during the transfer of information," says Professor Tarucha. He continues, "With power consumption becoming a major issue in modern electronics, valley current based devices open up a new direction for future ultra-low-power consumption computing devices."
Collaborating institutions
This research was conducted in collaboration with the Center for Emergent Matter Science (CEMS) RIKEN and National Institute for Materials Science.
unding
The researchers acknowledge support from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas 'Science of Atomic Layers', Canon Foundation, and DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation))-JST (Japan Science and Technology Agency) joint research project 'Nano Electronics'.
####
About University of Tokyo
The University of Tokyo is Japan's leading university and one of the world's top research universities. The vast research output of some 6,000 researchers is published in the world's top journals across the arts and sciences. Our vibrant student body of around 15,000 undergraduate and 15,000 graduate students includes over 2,000 international students. Find out more at www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/ or follow us on Twitter at @UTokyo_News_en.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Prof. Seigo Tarucha
Department of Applied Physics, Graduate School of Engineering, University of Tokyo
7-3-1, Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, 113-8656, Japan
Tel: +81-3-5841-6835
Fax: +81-3-5841-6835
Dr. Michihisa Yamamoto
Department of Applied Physics, Graduate School of Engineering, University of Tokyo
7-3-1, Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, 113-8656, Japan
Tel: +81-3-5841-6856
Fax: +81-3-5841-6842
Copyright © University of Tokyo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Journal article/Conference paper
Journal article/Conference paper
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








