Home > Press > Chemists discover key reaction mechanism behind the highly touted sodium-oxygen battery
 |
| Chemists at the University of Waterloo have discovered the key reaction that takes place in sodium-air batteries that could pave the way for development of the so-called holy grail of electrochemical energy storage. The key lies in Nazar's group discovery of the so-called proton phase transfer catalyst. By isolating its role in the battery's discharge and recharge reactions, Nazar and colleagues were not only able to boost the battery's capacity, they achieved a near-perfect recharge of the cell. When the researchers eliminated the catalyst from the system, they found the battery no longer worked. Unlike the traditional solid-state battery design, a metal-oxygen battery uses a gas cathode that takes oxygen and combines it with a metal such as sodium or lithium to form a metal oxide, storing electrons in the process. Applying an electric current reverses the reaction and reverts the metal to its original form. CREDIT:University of Waterloo |
Abstract:
Chemists at the University of Waterloo have discovered the key reaction that takes place in sodium-air batteries that could pave the way for development of the so-called holy grail of electrochemical energy storage.
Chemists discover key reaction mechanism behind the highly touted sodium-oxygen battery
Waterloo, Canada | Posted on May 28th, 2015Researchers from the Waterloo Institute for Nanotechnology, led by Professor Linda Nazar who holds the Canada Research Chair in Solid State Energy Materials, have described a key mediation pathway that explains why sodium-oxygen batteries are more energy efficient compared with their lithium-oxygen counterparts.
Understanding how sodium-oxygen batteries work has implications for developing the more powerful lithium-oxygen battery, which is has been seen as the holy grail of electrochemical energy storage.
Their results appear in the journal Nature Chemistry.
"Our new understanding brings together a lot of different, disconnected bits of a puzzle that have allowed us to assemble the full picture," says Nazar, a Chemistry professor in the Faculty of Science. "These findings will change the way we think about non-aqueous metal-oxygen batteries."
Sodium-oxygen batteries are considered by many to be a particularly promising metal-oxygen battery combination. Although less energy dense than lithium-oxygen cells, they can be recharged with more than 93 per cent efficiency and are cheap enough for large-scale electrical grid storage.
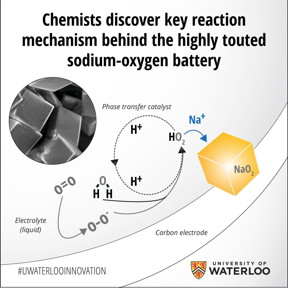
The key lies in Nazar's group discovery of the so-called proton phase transfer catalyst. By isolating its role in the battery's discharge and recharge reactions, Nazar and colleagues were not only able to boost the battery's capacity, they achieved a near-perfect recharge of the cell. When the researchers eliminated the catalyst from the system, they found the battery no longer worked.
Unlike the traditional solid-state battery design, a metal-oxygen battery uses a gas cathode that takes oxygen and combines it with a metal such as sodium or lithium to form a metal oxide, storing electrons in the process. Applying an electric current reverses the reaction and reverts the metal to its original form.
In the case of the sodium-oxygen cell, the proton phase catalyst transfers the newly formed sodium superoxide (NaO2) entities to solution where they nucleate into well-defined nanocrystals to grow the discharge product as micron-sized cubes. The dimensions of the initially formed NaO2 are critical; theoretical calculations from a group at MIT has separately shown that NaO2 is energetically preferred over sodium peroxide, Na2O2 at the nanoscale. When the battery is recharged, these NaO2 cubes readily dissociate, with the reverse reaction facilitated once again by the proton phase catalyst.
Chemistry says that the proton phase catalyst could work similarly with lithium-oxygen. However, the lithium superoxide (LiO2) entities are too unstable and convert immediately to lithium peroxide (Li2O2). Once Li2O2 forms, the catalyst cannot facilitate the reverse reaction, as the forward and reverse reactions are no longer the same. So, in order to achieve progress on lithium-oxygen systems, researchers need to find an additional redox mediator to charge the cell efficiently.
"We are investigating redox mediators as well as exploring new opportunities for sodium-oxygen batteries that this research has inspired," said Nazar."Lithium-oxygen and sodium-oxygen batteries have a very promising future, but their development must take into account the role of how high capacity - and reversibility - can be scientifically achieved."
###
Postdoctoral research associate Chun Xia along with doctoral students Robert Black, Russel Fernandes, and Brian Adams co-authored the paper.
The ecoENERGY Innovation Initiative program of Natural Resources Canada, and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada funded the project.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Nick Manning
226-929-7627
Copyright © University of Waterloo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








