Home > Press > Building quantum states with individual silicon atoms
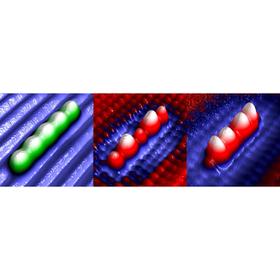 |
| Scanning tunnelling microscopy (STM) images of the quantum states of an artificial atomic defect structure in silicon. This structure was fabricated by using the STM to individually remove five hydrogen atoms from a hydrogen-terminated silicon (001) surface. The absence of the hydrogen atoms creates "dangling bond" states that interact to form extended, artificial molecular orbitals. Only the imaging bias voltage has been changed in the three images shown (from left to right, -1.4, +1.4, and +1.8 Volts). |
Abstract:
By introducing individual silicon atom 'defects' using a scanning tunnelling microscope, scientists at the London Centre for Nanotechnology have coupled single atoms to form quantum states.
Building quantum states with individual silicon atoms
London, UK | Posted on April 3rd, 2013Published today in Nature Communications, the study demonstrates the viability of engineering atomic-scale quantum states on the surface of silicon - an important step toward the fabrication of devices at the single-atom limit.
Advances in atomic physics now allow single ions to be brought together to form quantum coherent states. However, to build coupled atomic systems in large numbers, as required for applications such as quantum computing, it is highly desirable to develop the ability to construct coupled atomic systems in the solid state.
Semiconductors, such as silicon, routinely display atomic defects that have clear analogies with trapped ions. However, introducing such defects deterministically to observe the coupling between extended systems of individual defects has so far remained elusive.
Now, LCN scientists have shown that quantum states can be engineered on silicon by creating interacting single-atom defects. Each individual defect consisted of a silicon atom with a broken, or "dangling", bond. During this study, these single-atom defects were created in pairs and extended chains, with each defect separated by just under one nanometer.
Importantly, when coupled together, these individual atomic defects produce extended quantum states resembling artificial molecular orbitals. Just as for a molecule, each structure exhibited multiple quantum states with distinct energy levels.
The visibility of these states to the scanning tunneling microscope could be tuned through the variation of two independent parameters - the voltage applied to the imaging probe and its height above the surface.
The study was led by Dr Steven Schofield, who said: "We have created precise arrays of atomic defects on a silicon surface and demonstrated that they couple to form unique and interesting quantum states."
He added: "The next step is to replicate these results in other material systems, for example using substitutional phosphorus atoms in silicon, which holds particular interest for quantum computer fabrication."
Ongoing research at the LCN is exploring even more complex arrangements of these defects, including the incorporation of impurity atoms within the defect structures, which is expected to alter the symmetry of the defects (similar to the role of the nitrogen atom in the nitrogen-vacancy center defect in diamond).
####
About University College London - UCL
Founded in 1826, UCL was the first English university established after Oxford and Cambridge, the first to admit students regardless of race, class, religion or gender and the first to provide systematic teaching of law, architecture and medicine.
We are among the world's top universities, as reflected by our performance in a range of international rankings and tables. According to the Thomson Scientific Citation Index, UCL is the second most highly cited European university and the 15th most highly cited in the world.
UCL has nearly 25,000 students from 150 countries and more than 9,000 employees, of whom one third are from outside the UK. The university is based in Bloomsbury in the heart of London, but also has two international campuses – UCL Australia and UCL Qatar. Our annual income is more than £800 million.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Clare Ryan
UCL Media Relations Office
tel: +44 (0)20 3108 3846
mobile: +44 07747 556 056
out of hours +44 (0)7917 271 364
Copyright © University College London - UCL
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








