Home > Press > May the force be with the atomic probe: New models suggest devising means of probing a surface at a sub-micrometric level as this will help us understand how electrons’ diffusion affects long-range attractive forces
 |
Abstract:
Theoretical physicist Elad Eizner from Ben Gurion University, Israel, and colleagues created models to study the attractive forces affecting atoms located at a wide range of distances from a surface, in the hundreds of nanometers range. Their results, about to be published in EPJ D, show that these forces depend on electron diffusion, regardless of whether the surface is conducting or not. Ultimately, these findings could contribute to designing minimally invasive surface probes.
May the force be with the atomic probe: New models suggest devising means of probing a surface at a sub-micrometric level as this will help us understand how electrons’ diffusion affects long-range attractive forces
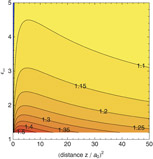
New York, NY and Heidelberg, Germany | Posted on December 21st, 2012Bombarding a surface with atoms helps us understand the distribution of its electrons and the structural arrangement of the surface atoms. The authors focused on understanding how a long-range force— referred to as the van der Waals-Casimir-Polder (vdW-CP) force — present between an atom and a surface allow us to distinguish surface characteristics on the basis of their conductivity.
A key factor in understanding the behaviour of the force, they realised, is the size of the electron cloud surrounding an impurity charge in the system. The latter depends both on the electrons' conductivity and their capability to diffuse in and along the surface.
They devised one model for the diffusion of the electronic charge in the bulk of the material and another one in the near-surface region. They tested their models on both conducting and non-conducting surfaces. They were thus able to explain why the atom-surface force shows a continuous transition in terms of conductivity between both types of surfaces.
For distances comparable to the size of the electron cloud spread, the strength of the vdW-CP attraction force, they found, can help distinguish between bulk and surface electrons diffusion. It could therefore be used as a probe. Potential applications exist, for example, in quantum computer hardware architectures focusing on the interface between different carriers of quantum bits of information.
Reference:
E.Eizner, B. Horovitz, and C. Henkel (2012), Van der Waals-Casimir-Polder interaction of an atom with a composite surface, European Physical Journal D, DOI: 10.1140/epjd/e2012-30294-x
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ann Koebler
49-622-148-78414
Copyright © Springer
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








