Home > Press > Research discovery could revolutionize semiconductor manufacture
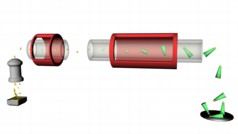 |
| Image: Aerotaxy production process |
Abstract:
A completely new method of manufacturing the smallest structures in electronics could make their manufacture thousands of times quicker, allowing for cheaper semiconductors. The findings have been published in the latest issue of Nature.
Instead of starting from a silicon wafer or other substrate, as is usual today, researchers have made it possible for the structures to grow from freely suspended nanoparticles of gold in a flowing gas.
Research discovery could revolutionize semiconductor manufacture
Lund, Sweden | Posted on November 29th, 2012 Behind the discovery is Lars Samuelson, Professor of Semiconductor Physics at Lund University, Sweden, and head of the University's Nanometre Structure Consortium. He believes the technology will be ready for commercialisation in two to four years' time. A prototype for solar cells is expected to be completed in two years.
"When I first suggested the idea of getting rid of the substrate, people around me said ‘you're out of your mind, Lars; that would never work'. When we tested the principle in one of our converted ovens at 400°C, the results were better than we could have dreamt of", he says.
"The basic idea was to let nanoparticles of gold serve as a substrate from which the semiconductors grow. This means that the accepted concepts really were turned upside down!"
Since then, the technology has been refined, patents have been obtained and further studies have been conducted. In the article in Nature, the researchers show how the growth can be controlled using temperature, time and the size of the gold nanoparticles.
Recently, they have also built a prototype machine with a specially built oven. Using a series of ovens, the researchers expect to be able to ‘bake' the nanowires, as the structures are called, and thereby develop multiple variants, such as p-n diodes.
A further advantage of the technology is avoiding the cost of expensive semiconductor wafers.
"In addition, the process is not only extremely quick, it is also continuous. Traditional manufacture of substrates is batch-based and is therefore much more time-consuming", adds Lars Samuelson.
At the moment, the researchers are working to develop a good method to capture the nanowires and make them self-assemble in an ordered manner on a specific surface. This could be glass, steel or another material suited to the purpose.
The reason why no one has tested this method before, in the view of Professor Samuelson, is that today's method is so basic and obvious. Such things tend to be difficult to question.
However, the Lund researchers have a head start thanks to their parallel research based on an innovative method in the manufacture of nanowires on semiconductor wafers, known as epitaxy - consequently, the researchers have chosen to call the new method aerotaxy. Instead of sculpting structures out of silicon or another semiconductor material, the structures are instead allowed to develop, atomic layer by atomic layer, through controlled self-organisation.
The structures are referred to as nanowires or nanorods. The breakthrough for these semiconductor structures came in 2002 and research on them is primarily carried out at Lund, Berkeley and Harvard universities.
The Lund researchers specialise in developing the physical and electrical properties of the wires, which helps create better and more energy-saving solar cells, LEDs, batteries and other electrical equipment that is now an integrated part of our lives.
The article ‘Continuous gas-phase synthesis of nanowires with tuneable properties' can be found by entering "I 10.1038/nature11652" here: http://dx.doi.org/.
Besides Lars Samuelson, the other authors of the article are: Magnus Heurlin, Martin Magnusson, David Lindgren, Martin Ek, Reine Wallenberg and Knut Deppert, all employed at Lund University, except for Martin Magnusson, who works at start-up company Sol Voltaics AB.
The research has been funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research (SSF), the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation and Vinnova.
####
About Lund University
Lund University seeks to be a world-class university that works to understand, explain and improve our world and the human condition. The University is ranked as one of the top 100 in the world. We tackle complex problems and global challenges and work to ensure that knowledge and innovations benefit society. We provide education and research in engineering, science, law, social sciences, economics and management, medicine, humanities, theology, fine art, music and drama.
Our 47 000 students and 6 800 employees are based at our campuses in Lund, Malmö and Helsingborg. The University has a turnover of around EUR 700 million (or USD 900 million), of which two thirds is in research and one third in education.
About semiconductors
Semiconductors are materials that neither conduct electricity as well as metals, nor stop a current as effectively as insulators – silicon and germanium are two examples. These properties may not sound attractive, but in actual fact they are excellent. The reason is that we can influence the conductive capacity of the materials, for example by introducing impurity atoms, known as doping. Materials with different types of doping can be combined to manufacture products such as transistors, solar cells or LEDs.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lars Samuelson
+46 46 222 76 79
+46-703-177-679
Copyright © Lund University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Contact details for the other authors can be found by searching on www.lunduniversity.lu.se:
Contact details for the other authors can be found by searching on www.lunduniversity.lu.se:
![]() Lund University Nanometre Structure Consortium, nmC@LU:
Lund University Nanometre Structure Consortium, nmC@LU:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








