Home > Press > Nanoscientists find long-sought Majorana particle
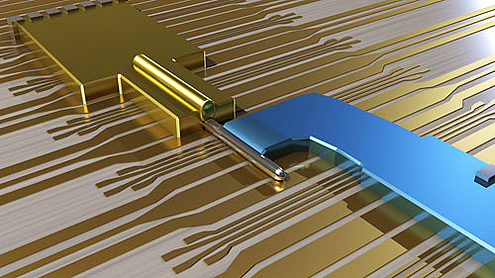 |
| The device is made of an Indium Antemonide nanowire, covered with a Gold contact and partially covered with a Superconducting Niobium contact. The Majorana fermions are created at the end of the Nanowire. |
Abstract:
Scientists at TU Delft's Kavli Institute and the Foundation for Fundamental Research on Matter (FOM Foundation) have succeeded for the first time in detecting a Majorana particle. In the 1930s, the brilliant Italian physicist Ettore Majorana deduced from quantum theory the possibility of the existence of a very special particle, a particle that is its own anti-particle: the Majorana fermion. That ‘Majorana' would be right on the border between matter and anti-matter.
Nanoscientists find long-sought Majorana particle
The Netherlands | Posted on April 16th, 2012Nanoscientist Leo Kouwenhoven already caused great excitement among scientists in February by presenting the preliminary results at a scientific congress. On 12 April, the scientists will publish their research in Science. The research was financed by the FOM Foundation and Microsoft.
Quantum computer and dark matter
Majorana fermions are very interesting - not only because their discovery opens up a new and uncharted chapter of fundamental physics; they may also play a role in cosmology. A proposed theory assumes that the mysterious ‘dark matter, which forms the greatest part of the universe, is composed of Majorana fermions. Furthermore, scientists view the particles as fundamental building blocks for the quantum computer. Such a computer is far more powerful than the best supercomputer, but only exists in theory so far. Contrary to an ‘ordinary' quantum computer, a quantum computer based on Majorana fermions is exceptionally stable and barely sensitive to external influences.
Nanowire
For the first time, scientists in Leo Kouwenhoven's research group managed to create a nanoscale electronic device in which a pair of Majorana fermions ‘appear' at either end of a nanowire. They did this by combining an extremely small nanowire, made by colleagues from Eindhoven University of Technology, with a superconducting material and a strong
magnetic field. ‘The measurements of the particle at the ends of the nanowire cannot otherwise be explained than through the presence of a pair of Majorana fermions', says Leo Kouwenhoven..
Particle accelerators
It is theoretically possible to detect a Majorana fermion with a particle accelerator such as the one at CERN. The current Large Hadron Collider appears to be insufficiently sensitive for that purpose but, according to physicists, there is another possibility: Majorana fermions can also appear in properly designed nanostructures. ‘What's magical about quantum mechanics is that a Majorana particle created in this way is similar to the ones that may be observed in a particle accelerator, although that is very difficult to comprehend', explains Kouwenhoven. ‘In 2010, two different groups of theorists came up with a solution using nanowires, superconductors and a strong magnetic field. We happened to be very familiar with those ingredients here at TU Delft through earlier research.' Microsoft approached Leo Kouwenhoven to help them lead a special FOM programme in search of Majorana fermions, resulting in a successful outcome..
Ettore Majorana
The Italian physicist Ettore Majorana was a brilliant theorist who showed great insight into physics at a young age. He discovered a hitherto unknown solution to the equations from which quantum scientists deduce elementary particles: the Majorana fermion. Practically all theoretic particles that are predicted by quantum theory have been found in the last decades, with just a few exceptions, including the enigmatic Majorana particle and the well-known Higgs boson. But Ettore Majorana the person is every bit as mysterious as the particle. In 1938 he withdrew all his money and disappeared during a boat trip from Palermo to Naples. Whether he killed himself, was murdered or lived on under a different identity is still not known. No trace of Majorana was ever found.
References
The article is published in Science Express on 12 April: Signatures of Majorana fermions in hybrid superconductor-semiconductor nanowire devices, V. Mourik1†, K. Zuo1†, S.M. Frolov1, S.R. Plissard2, E.P.A.M. Bakkers1,2, L.P. Kouwenhoven1*
1Kavli Institute of Nanoscience, TU Delft, 2600 GA Delft.
2Department of Applied Physics, TU Eindhoven, 5600 MB Eindhoven.
†These authors contributed equally.
*E-mail:
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Copyright © TU Delft
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








