Home > Press > Ferroelectric oxides do the twist
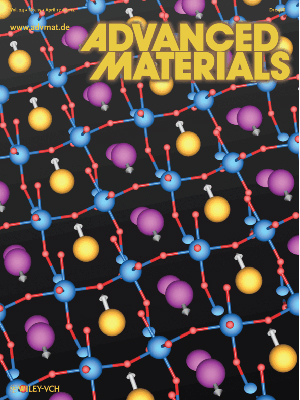 |
| Advanced Materials Engineered electric polarizations are indicated by the gray arrows, a "twisting-like" distortion of the corner-connected oxygen octahedral that is common to many perovskite oxides. First-principles calculations reveal that carefully designed atomic layering, represented by alternating gold and magenta spheres forming an atomic-scale superlattice, allows the octahedral rotations to induce ferroelectricity. |
Abstract:
Some materials, by their nature, do what we want them to do -- notably, the ubiquitous, semiconducting silicon found in almost every electronic device. But sometimes, naturally occurring materials need a little nudge -- or in the case of recent Cornell research, a twist -- to make them useful.
Ferroelectric oxides do the twist
Ithaca, NY | Posted on April 11th, 2012Assistant professor of applied and engineering physics Craig Fennie and Drexel University's James Rondinelli have published a method for turning a class of ceramic materials called perovskites into a material that's ferroelectric. The work was published April 10 by Advanced Materials and also will be featured on the printed journal's inside cover.
Ferroelectricity is a property in which a spontaneous electric polarization can be flipped by applying a small electric field, useful for low-power memory and switching devices. Traditional ferroelectric mechanisms, however, are often chemically incompatible with such phenomena as ferromagnetism, limiting their use in new types of multifunctional devices.
The researchers' theory-only work, which employed density functional calculations, concluded that ferroelectricity in perovskites can be realized if their atomic structures are manipulated at the nanometer length scale and by slicing them only a few atoms thin, letting the natural twisting of their corner-shared octahedra -- the basic structural unit of perovskite crystals -- do the rest.
The researchers' engineered electric polarizations are the result of stacking chemically different perovskites into atomically thin striped-patterns, which allow their normal rotational patterns to induce ferroelectricity.
"In the past, those rotations and tilts didn't do anything, but by combining them in this way, they can be coupled to an electric field through polarization," Fennie said. "This is the first step in the broad field of using rotations that couple to an applied electric field to control the properties of materials."
Fennie and Rondinelli transformed their theoretical conclusions into experimental guidelines for chemists and materials scientists, with the goal of enabling ferroelectric materials by design.
"The strategy we applied in this work provides a framework for rapid materials discovery of functional properties in a variety of crystal families in advance of materials synthesis," Rondinelli said.
According to Fennie, the work illustrates that theory will play a pivotal role in identifying new material systems for integration into next-generation technologies; theoretical studies of materials are no longer limited to after-the-fact analysis of experimental data.
The research was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Basic Energy Sciences.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Anne Ju
Chronicle Online
312 College Ave.
Ithaca, NY 14850
607.255.4206
Copyright © Cornell University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








