Home > Press > Gold nanoantennas detect proteins: New method of monitoring protein molecules using gold nanoparticles
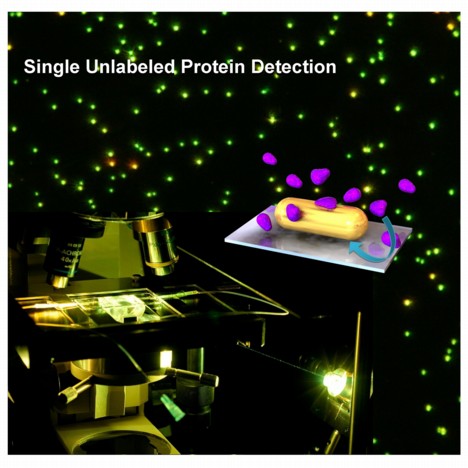 |
| Institute of Physical Chemistry The new method developed in Mainz makes it possible to observe individual protein molecules under a microscope with the help of a gold nanoparticle (diagram: Gold nanoantenna with protein molecules shown in purple). |
Abstract:
Scientists at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) in Germany have developed a new method of observing individual proteins. Detailed knowledge of the dynamics of proteins is necessary in order to understand the related biological processes that occur on the molecular level. To date, this information has been obtained by means of labeling proteins with fluorescent substances, but unfortunately this changes the proteins under investigation and thus influences the biological processes that are to be observed. "Our method allows live tracking of individual proteins without having to label them first," explains Professor Dr. Carsten Sönnichsen of the Institute of Physical Chemistry at JGU. "We are now gaining entirely new insights into molecular processes and can see, for example, how things are constantly in motion even on the very smallest scale."
Gold nanoantennas detect proteins: New method of monitoring protein molecules using gold nanoparticles
Mainz, Germany | Posted on March 14th, 2012The method developed by the group of Mainz chemists led by Carsten Sönnichsen is based on the use of gold nanoparticles. These serve as glistening nanoantennas that, when they detect individual unlabeled proteins, slightly change their frequency or, in other words, their color. These tiny color changes can be observed using the technique developed in Mainz. "This is an enormous leap forward technologically: We have managed to achieve a very high time resolution for the observation of individual molecules," says Sönnichsen. It is thus now possible to precisely observe the dynamics of a protein molecule down to the millisecond.
The opportunity to detect individual protein molecules also opens up completely new horizons. It has thus become practicable to track the fluctuation of protein population densities and observe protein adsorption processes in real time, among other things. "We can see how molecules move, how they dock at particular locations, and how they fold - this has given us a window into the molecular world," explains Dr. Irene Ament, a member of Sönnichsen's group. This new technology may prove to be useful not only in chemistry but also in medicine and biology.
The work is an important element in research into non-equilibrium phenomena at the molecular level and thus provides a solid foundation for the planned Cluster of Excellence Molecularly Controlled Non-Equilibrium (MCNE), which has been selected to enter the final round of the Excellence Initiative by the German federal and state governments to promote top-level research at German universities. Among other sources, the project received financial support in the form of an ERC Starting Grant for the project "Single metal nanoparticles as molecular sensors" (SINGLESENS).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Professor Dr. Carsten Sönnichsen
Institute of Physical Chemistry
Johannes Gutenberg University
D 55099 Mainz
Tel +49 6131 39-24313
Fax +49 6131 39-26747
Copyright © Johannes Gutenberg Universitaet Mainz
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








