Home > Press > Carnegie Mellon Scientists Create Toolbox Of Fluorescent Probes in a Rainbow of Colors
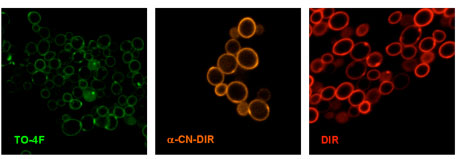 |
| The above figure illustrates three populations of yeast cells labeled with green, orange and red fluoromodules expressed on the cell surface. |
Abstract:
Scientists at Carnegie Mellon University's Department of Chemistry and Molecular Biosensor and Imaging Center (MBIC) are advancing the state-of-the-art in live cell fluorescent imaging by developing a new class of fluorescent probes that span the spectrum — from violet to the near-infrared.
Carnegie Mellon Scientists Create Toolbox Of Fluorescent Probes in a Rainbow of Colors
San Francisco, CA | Posted on March 26th, 2010The new technology, called fluoromodules, can be used to monitor biological activities of individual proteins in living cells in real time. At the 239th national meeting of the American Chemical Society, Carnegie Mellon chemists and MBIC scientists will discuss recent advances in their fluoromodule technology that have produced diverse and photostable probes.
Fluoromodules, which consist of dye-protein complexes, provide alternatives to common fluorescent proteins, such as Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP), but with a wider selection of colors and the potential for significantly greater photostability, which allows scientists to image the dye for longer periods of time. This is made possible by the fact that the dye is noncovalently bound to the protein, which allows fresh dye to replace bleached dye.
"We initially isolated and characterized fluoromodules that generate fluorescence from the fluorogenic dyes thiazole orange and malachite green. We are now expanding our repertoire by synthesizing new dyes that emit in the orange and violet regions of the spectrum, and engineering proteins that bind to the new dyes with great affinity," said Chemistry Professor Bruce Armitage, co-director of the Center for Nucleic Acid Science and Technology at Carnegie Mellon and a member of the MBIC team developing the fluoromodules.
Fluoromodules are made of a fluorogen-activating protein (FAP) and a non-fluorescent dye called a fluorogen. The FAP, which is genetically expressed in a cell and tagged to a protein of interest, does not become fluorescent until it binds with its fluorogen. With the novel FAPs and associated fluorogens created by the MBIC team, the researchers can control when a target protein lights up, allowing them to track proteins on the cell surface and within living cells in very simple and direct ways, eliminating cumbersome experimental steps.
Recent advances in the MBIC fluoromodule technology being presented at the ACS meeting include:
> Working with a FAP that had a low affinity for the fluorogenic dye dimethlindole red (DIR), graduate student Hayriye Özhalici-Ünal used PCR mutagenesis to introduce mutations into the FAP's genetic sequence. A small number of mutations increased several-fold the protein's affinity for DIR, enabling very specific and selective binding of the FAP to its dye partner (DIR). Özhalici-Ünal will present this work at 9:50 a.m., Thursday, March 25 during the Follow-on Biologics: Protein Engineering session located in room 201 West Bldg. in the Moscone Center.
> Graduate student Nathaniel Shank synthesized a modified DIR, making it eight-times more photostable. This significant improvement could have an impact on single molecule imaging. Additionally, the modified DIR emits in the orange range of the spectrum, adding another color to the fluoromodule toolkit being developed at MBIC. Shank will present this work at 8 p.m., Tuesday, March 23 during the Total Synthesis of Complex Molecules, Material Devices & Switches, Physical Organic Chemistry poster session located in Hall D of the Moscone Center.
> By synthesizing a new dye and identifying FAPs that bind to it, research chemist Gloria Silva and graduate student Kim Zanotti developed a fluoromodule that emits fluorescence in the violet, which is a welcome addition to a very limited number of probes able to emit in the violet portion of the spectrum. Zanotti will present this work a 6 p.m., Tuesday, March 23 during the poster session located in room 3009/3011 West Bldg. in the Moscone Center.
The aforementioned work, funded by the Pennsylvania Department of Health and the National Institutes of Health (NIH), is part of the mission of the NIH National Technology Center for Networks and Pathways. The effort, headquartered at Carnegie Mellon, is a partnership between Carnegie Mellon and the University of Pittsburgh. For more information, visit www.mbic.cmu.edu/
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jocelyn Duffy
412-268-9982
Copyright © Carnegie Mellon University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








