Home > Press > CNT Defects = Better Energy Storage?
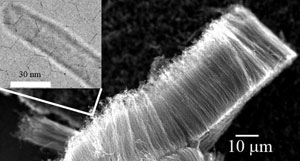 |
| Carbon nanotubes could serve as supercapacitor electrodes with enhanced charge and energy storage capacity (inset: a magnified view of a single carbon nanotube). |
Abstract:
UCSD Researchers Discover That Defects in Carbon Nanotubes Could Lead to Improved Charge and Energy Storage Systems
CNT Defects = Better Energy Storage?
La Jolla, CA | Posted on November 24th, 2009Most people would like to be able to charge their cell phones and other personal electronics quickly and not too often. A recent discovery made by UC San Diego engineers could lead to carbon nanotube-based supercapacitors that could do just this.
In recent research, published in Applied Physics Letters, Prabhakar Bandaru, a professor in the UCSD Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, along with graduate student Mark Hoefer, have found that artificially introduced defects in nanotubes can aid the development of supercapacitors.
"While batteries have large storage capacity, they take a long time to charge; while electrostatic capacitors can charge quickly but typically have limited capacity. However, supercapacitors/electrochemical capacitors incorporate the advantages of both," Bandaru said.
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have been generally hailed as one of the wonder materials of the 21st century and have been widely recognized as ushering in the nanotechnology revolution. They are cylindrical structures, with diameters of 1 to 100 nanometers, that have been suggested to have outstanding structural, chemical, and electrical, characteristics based on their atomically perfect structures with a large surface area-to-volume ratio. However, defects are inevitable in such a practical structure, an aspect that was first investigated by UCSD engineering graduate student Jeff Nichols and then substantially extended by Hoefer in Bandaru's lab.
"We first realized that defective CNTs could be used for energy storage when we were investigating their use as electrodes for chemical sensors," Hoefer said. "During our initial tests we noticed that we were able to create charged defects that could be used to increase CNT charge storage capabilities."
Specifically, defects on nanotubes create additional charge sites enhancing the stored charge. The researchers have also discovered methods which could increase or decrease the charge associated with the defects by bombarding the CNTs with argon or hydrogen.
"It is important to control this process carefully as too many defects can deteriorate the electrical conductivity, which is the reason for the use of CNTs in the first place. Good conductivity helps in efficient charge transport and increases the power density of these devices," Bandaru added.
"At the very outset, it is interesting that CNTs, which are nominally considered perfect, could be useful with so many incorporated defects," he added.
The researchers think that the energy density and power density obtained through their work could be practically higher than existing capacitor configurations which suffer from problems associated with poor reliability, cost, and poor electrical characteristics.
Bandaru and Hoefer hope that their research could have major implications in the area of energy storage, a pertinent topic of today. "We hope that our research will spark future interest in utilizing CNTs as electrodes in charge storage devices with greater energy and power densities," Hoefer said.
While more research still needs to be done to figure out potential applications from this discovery, the engineers suggest that this research could lead to wide variety of commercial applications, and hope that more scientists and engineers will be compelled to work in this area, Bandaru said.
Meanwhile, Hoefer said this type of research will help fuel his future engineering career.
"It is remarkable how current tools and devices are becoming increasing more efficient and yet smaller due to discoveries made at the nanoscale," he said. "My time spent investigating CNTs and their potential uses at the Jacobs School will prepare me for my career, since future research will continue the trend of miniaturization while increasing efficiency."
"Determination and enhancement of the capacitance contributions in carbon nanotube based electrode systems," Applied Physics Letters. M. Hoefer and P.R. Bandaru, Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Materials Science Program, University of California, San Diego.
####
About University of California, San Diego
UC San Diego is dedicated to the advancement of knowledge through excellence in education and research at the undergraduate, graduate, professional school and postdoctoral levels. The campus is committed to community engagement, public service and industry partnerships in order to advance the health and well-being of our region, state, nation and the world. Our academic community of world-renowned faculty, bright students and dedicated staff is characterized by a culture of interdisciplinary collaboration and innovation which spans the globe.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Andrea Siedsma
858-822-0899
Copyright © University of California, San Diego
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








